A seamless and robust network connection forms the backbone of our daily activities in today’s digital era – And the essential component of these network connections are none other than “CABLES” that transmit data at incredible speeds.
Two predominant players in this arena are ONT (Optical Network Terminal) cables and Ethernet cables. While both are instrumental in shaping our digital experiences, they have distinct roles and functionalities in the realm of modern networking.
Briefly, an ONT is a modem that uses optical fiber cables that bridge the internet connection from an ISP (internet service provider) to the end user of fiber internet, while Ethernet cables are used to connect the ONT device to your router that provides internet in your home and offices.
Understanding the differences between these two types of cables is not just a matter of technical curiosity; it’s paramount for ensuring optimal network performance.
Whether you’re setting up a new office, optimizing your home’s internet, or just curious about the tech behind your screens, delving into the world of ONT and Ethernet can offer valuable insights.
Read till the end as we unravel the intricacies of these essential network components.
Before we start off with the discussion on ONT cable vs ethernet cables, let’s have a brief introduction to “ONT”.
What is ONT (Optical Network Terminal)?
So, An Optical Network Terminal (ONT) is an essential device within the framework of a fiber-optic broadband connection. Positioned at the subscriber’s location, whether a home, office or any other setting, the ONT serves as a critical bridge. Its primary responsibility is to transform the incoming optical signals from the fiber-optic cable into electrical signals that standard devices can process and use. These devices range from computers and televisions to telephones.
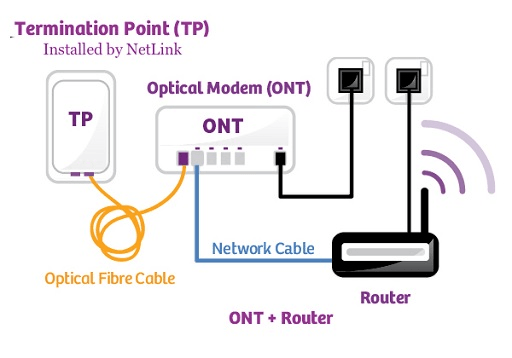
In terms of its build, the ONT is equipped with dual interfaces. The optical interface directly connects to the fiber network, facilitating a communication link with the service provider’s central system, known as the Optical Line Terminal (OLT). This connection is bridged through an optical fiber cable, so here we can name the cable as “ONT cable.” Meanwhile, the electrical interface connects to the end-user’s devices. This interface needs an ethernet cable or a network cable to connect with end-user devices like mobile, laptops, etc.
This leads to our main discussion on ONT cables vs. ethernet cables, so let’s get started.
ONT Cables – A Detailed Overview
“ONT Cable”- A Misconception
First and foremost, it’s vital to clarify a common misconception: the term “ONT cables” is a misnomer. The ONT itself is a device, and it doesn’t come with its own unique type of cable. Instead, the ONT uses standard fiber-optic cables to connect to the broader network. When people refer to “ONT cables,” they are typically talking about the fiber-optic cables that link the ONT to the network.
Construction and Build
These fiber-optic cables are marvels of modern engineering. Composed of strands of glass or plastic fibers, they transmit data as light signals. This method of data transmission is what allows fiber-optic connections to achieve much higher speeds than traditional copper cables. Each strand is incredibly thin, roughly the diameter of a human hair, and can carry a significant amount of data. To protect these strands, they are usually encapsulated in multiple layers of protective material.
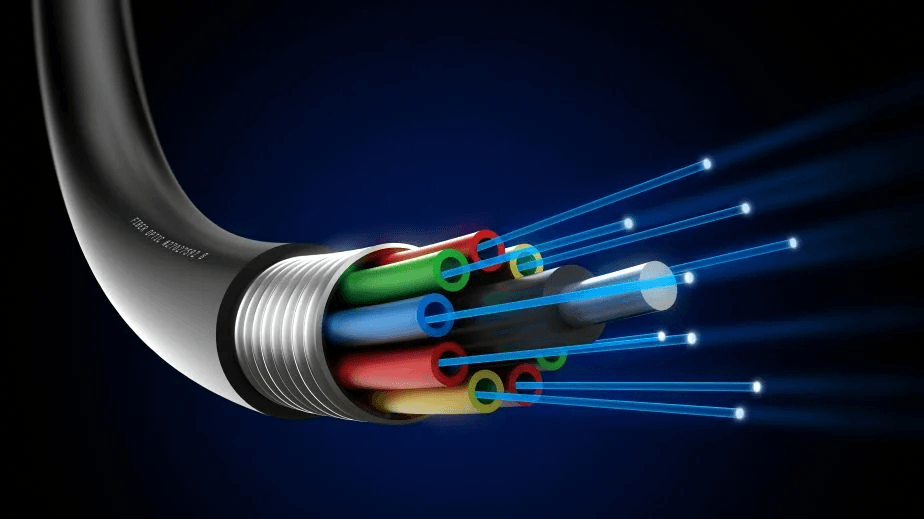
What is the function of an ONT Cable?
The ONT’s primary function is to convert the optical signals carried by these cables into electrical signals that can be understood and utilized by household or commercial digital devices. Conversely, it translates electrical signals from your devices back into optical signals for transmission over the fiber-optic network.
The connectivity process is relatively straightforward. The service provider’s main network connects to the ONT using a fiber-optic cable. From the ONT, other types of connections (like Ethernet) distribute the signal to various devices in a household or commercial establishment.
Moving to the next part of the discussion, the ethernet cables, let’s dig in and find out everything about them.
Ethernet Cable – An In-Depth Insight
The Ethernet cable, a staple in modern-day computing and networking, is emblematic of the world’s digital connectivity. While wireless connections have gained massive popularity, the reliability, speed, and security of a hard-wired Ethernet connection remain unmatched in many applications.
At its core, an Ethernet cable is designed to connect devices within a local area network (LAN), such as computers, routers, and switches. By doing so, it facilitates the transmission of data over short to medium distances, ensuring consistent connectivity and data exchange.
Construction and Build
The construction of an Ethernet cable is intricate. Typically, it consists of multiple twisted pairs of copper wires, each encased in its own insulation. The twisting pattern is not random; it serves to reduce interference from both external sources and adjacent pairs within the same cable. Depending on the type and category of the cable, the number of twists per inch and overall design can vary.
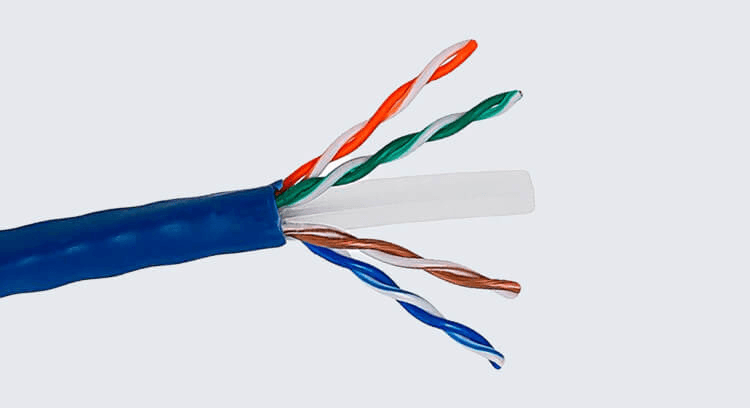
Denotation Of Different Categories Of Ethernet Cables
Over time, Ethernet cables have evolved, leading to the introduction of different categories. Each category, often denoted as “Cat” followed by a number (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7), indicates the cable’s performance specifications.
Higher numbers generally signify better performance, with increased data transfer rates and bandwidth. For instance, while a Cat5e cable might support speeds up to 1 Gbps, a Cat6a can push this to 10 Gbps with a suitable network setup.
Standout Features Of Ethernet Cables
One of the standout features of Ethernet cables is their resistance to latency and interference, especially when compared to wireless connections. The physical connection ensures that data packets arrive at their destination more consistently, making it the preferred choice for applications where real-time data transfer is paramount, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
ONT vs. Ethernet Cables: Key Differences Between Them
Let’s dive into the key differences between an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) and Ethernet cables based on the different categories:
Data Transmission Methods:
- ONT (Optical Network Terminal): ONTs use light-based data transmission through fiber optic cables. They convert optical signals into electrical signals for user devices, and vice versa, using light pulses for communication.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables use electrical signals to transmit data. These signals travel along twisted pairs of copper wires within the cable.
Speed and Bandwidth Capacities:
- ONT: Fiber optic connections through ONTs can provide very high-speed data transmission, commonly ranging from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps and beyond.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables can provide varying speeds depending on the cable category, ranging from 10 Mbps (older categories) to 10 Gbps or more (higher categories like Cat6a or Cat7).
Distance Limitations and Signal Attenuation:
- ONT: Fiber optics have significantly lower signal attenuation compared to copper Ethernet cables, allowing data to be transmitted over much longer distances without significant loss of signal quality.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cable distances are limited due to signal degradation and interference, especially at higher data rates. Longer distances may require signal boosters or repeaters.
Cost Considerations:
Initial Investment:
- ONT: Setting up fiber optic infrastructure, including ONTs, can involve higher initial costs due to the specialized equipment and cabling required.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables, being based on existing copper infrastructure, can have lower initial setup costs for shorter distances and lower data rates.
Maintenance and Replacement Costs:
- ONT: Fiber optic cables are generally more robust and require less maintenance compared to Ethernet cables. Fiber is less prone to interference and physical damage.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables may require more maintenance, especially in environments prone to electromagnetic interference or physical wear and tear.
Deployment Scenarios:
- ONT: ONTs are commonly used in scenarios where high-speed, long-distance data transmission is crucial, such as connecting homes and businesses to fiber-optic-based broadband services. They are also used in large-scale telecommunications networks and data centers.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables are widely used in local area networks (LANs) within offices, homes, and small businesses, where moderate data speeds and shorter distances are sufficient.
Interplay Between ONT and Ethernet in Many Networks:
In many modern network setups, ONT cables and Ethernet cables can work together to provide a comprehensive solution. For example, an ONT can be used to establish a high-speed fiber optic connection at a central point (like a building’s entrance), and then Ethernet cables can be used to distribute the connection to individual devices within the building.
Making the Right Choice: ONT Cable or Ethernet Cable
In making the right choice between ONT (Optical Network Terminal) cables and Ethernet cables, understanding their unique strengths is key. ONT cables shine in high-speed, long-distance data transmission through fiber optics, ideal for large-scale networking and remote connections. Conversely, Ethernet cables thrive in local networks, offering reliable connectivity for shorter distances.
Future-proofing is another crucial aspect, considering the potential for scalability, upgrades, and evolving technology standards. Careful consideration of your requirements will help you harness the power of both technologies, ensuring seamless and efficient connectivity tailored to your specific needs.
FAQs:
1- Does fiber optic cable outperform Ethernet?
Indeed, fiber optic cable surpasses Ethernet in several aspects. Notably, fiber optics excels in terms of data transfer speeds, bandwidth capacity, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Its ability to transmit data over longer distances with minimal signal loss makes it superior for high-speed, long-range networking needs. However, Ethernet cables remain practical for local networks and short distances due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of use.
2- What is the main difference between ONT cables and Ethernet cables?
The main difference lies in their data transmission methods. ONT (Optical Network Terminal) cables utilize light-based transmission through fiber optics, while Ethernet cables transmit data using electrical signals through copper wires.
3- Which one is better for long-distance connections: ONT or Ethernet cables?
A2: For long-distance connections, ONT cables are the better choice. They offer significantly lower signal attenuation over extended distances due to their fiber optic technology, making them ideal for maintaining signal quality over vast distances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you must have learned much about ONT (Optical Network Terminal) cables and Ethernet cables and their distinct advantages. ONT cables excel in high-speed, long-distance data transmission through fiber optics, while Ethernet cables are practical for local networks. Their synergy forms the foundation of modern networking, combining ONTs’ long-range prowess with Ethernet’s localized efficiency, ensuring tailored and effective connectivity solutions for evolving technological needs.
While connecting over cables can provide reliable and consistent signals, sometimes a wireless solution is essential – especially in setups requiring flexibility or portability. A wireless video transmitter is a great alternative, enabling you to transmit high-quality video signals without being limited by lengthy cables or complicated installations.






























.png)