The microphone’s directionality or polar patterns define the specific characteristics of how it will capture the sound. The pickup pattern is the building block of mics, allowing them to capture the whispers or reject the audible sounds.
Therefore, two microphone categories, omnidirectional and unidirectional, stand out because of their unique characteristics and capture patterns. Also, knowing the difference between these mics will amplify the quality of your recordings. So, the microphone’s distinct pickup patterns are crucial to understand before selection.
The pickup patterns of microphones and how the microphone works
The microphone pickup pattern is a sensitive place to capture sound within its range. Therefore, every microphone will pick the sound source from its diaphragm according to its directionality. So, based on their sensitivity, microphones are categorized into three pickup patterns: unidirectional, bidirectional, and omnidirectional.
Unidirectional Microphones
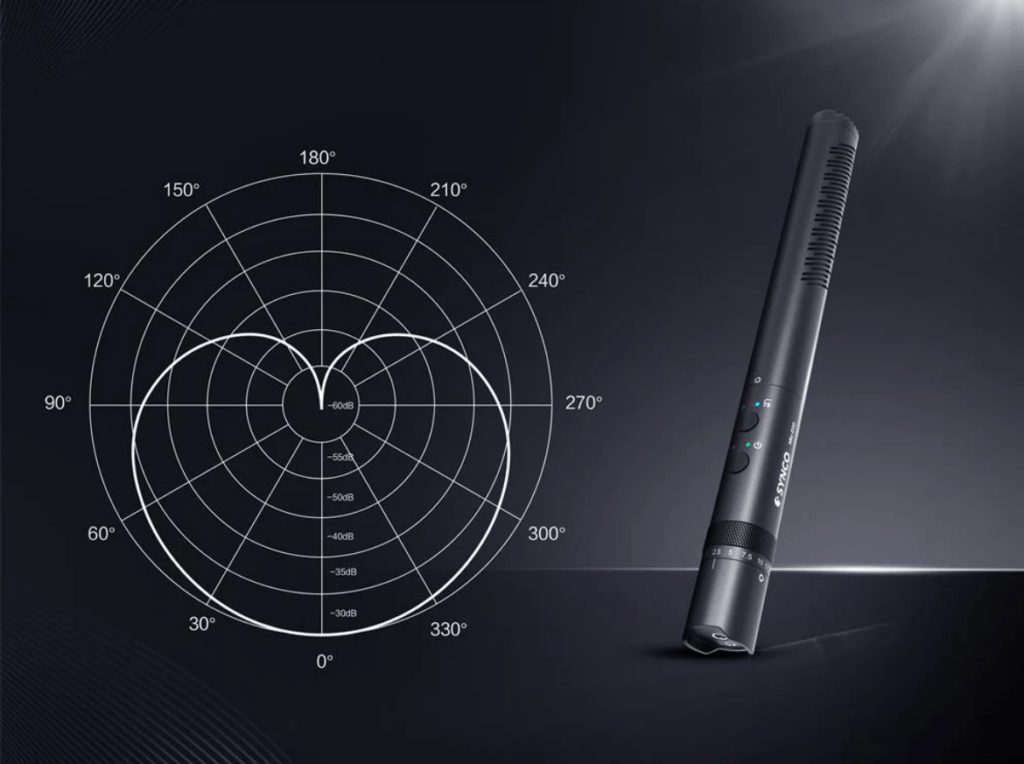

With their higher sensitivity to the actual sound source, these mics accept sounds from one direction and reject voices from rear surroundings. So, ensure to point the mic accurately to the voice source, and other noises will not interfere.
Bidirectional Microphones
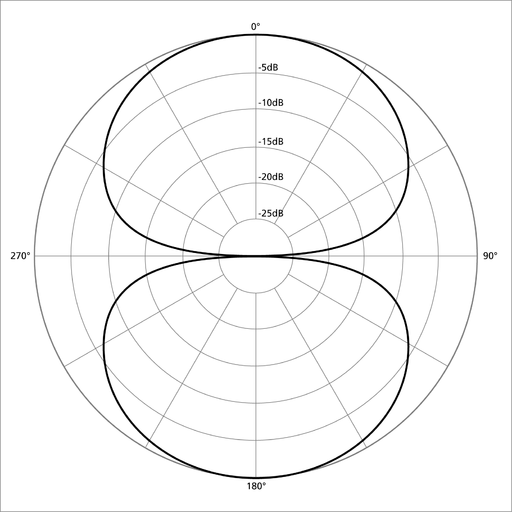
Bidirectional microphones are perfect for recording between two sound sources, such as during the interviews. These mics can be recorded from two opposite directions and provide excellent results in home studios.
Omnidirectional Microphones
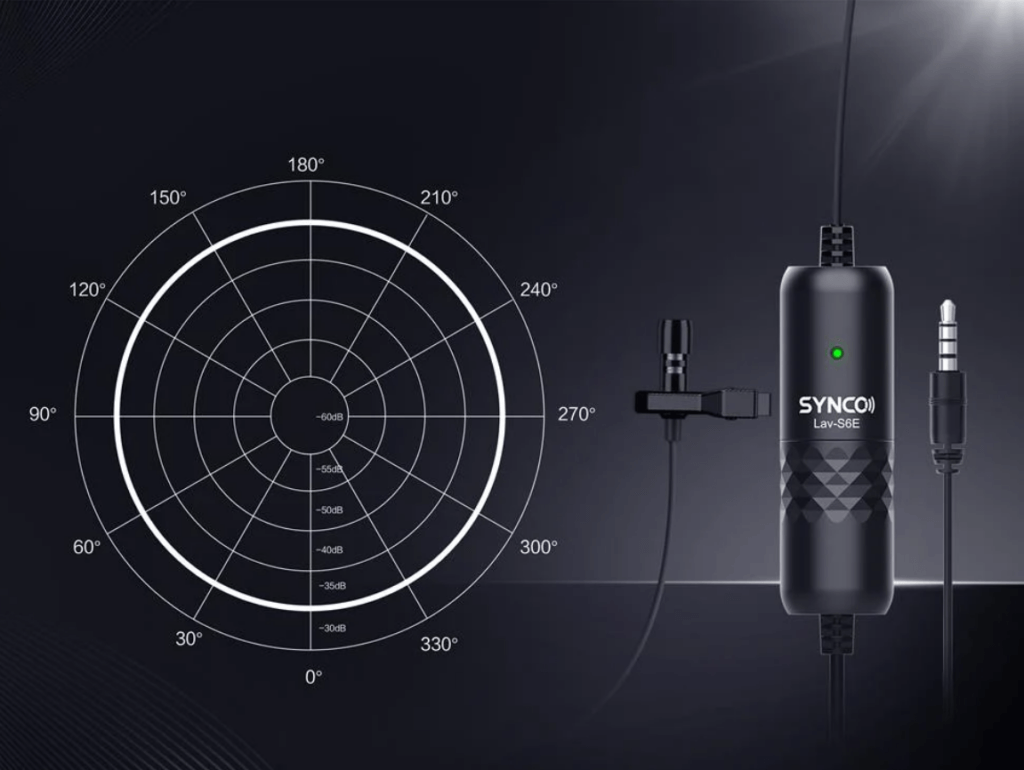

The microphones are susceptible to picking up sounds from every direction and capture crisp, clear voices. Because of their unique pickup patterns, it’s essential to use them wisely to avoid unwanted noises.
Every microphone has its specific pickup pattern, so they are different in recording and producing crisp, clear audio. The polar patterns only indicate the direction of the mic to capture the audio and do not guarantee the quality.
Microphones have sensitive and different polar patterns, so changing or fixing the post-production patterns is impossible. Therefore, it’s essential to consider your required microphone that can suffice your needs carefully.
How do microphones work?
Despite their differences, all microphones are transducers with their shared ability to convert sound waves into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified back to the audible sound with the help of amplifiers. Commonly used dynamic microphones work on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
- The sound waves cause the thin diaphragm to move. The diaphragm is surrounded by the magnet and is attached to the coil.
- The diaphragm movements create magnetic fields around the coil, which moves the mic coil, creating electrical current according to sound waves.
What are omnidirectional microphones?
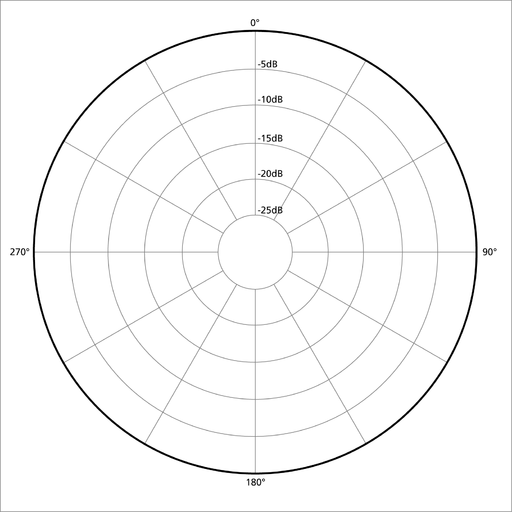
The omnidirectional mics capture quality sounds from every direction with their high sensitivity. Because the microphones do not have a specific pickup pattern, they provide quality recordings for conferences or public meetings.
It’s exceptional in studio environments with multiple musicians and helps edit post-production recordings. These mics ensure equal gains by sensitively collecting the audio from every direction.
- Omnidirectional mics are superior due to their crisp, clear audio and can be used upside down without impacting the quality.
- The mic is ideal for recording background noises during conferences and has no definite audio source.
- Because it captures from all directions, it is difficult to isolate different channels, and the ratio of indirect to direct sound will not be possible.
Pros:
- Pick sounds equally from all directions
- It does not have a proximity effect
- It does not have the effect of handling or wind noises
- Perfect for stereo recording
Cons:
- Unable to isolate different channel source
- No channel isolation
What are unidirectional microphones?
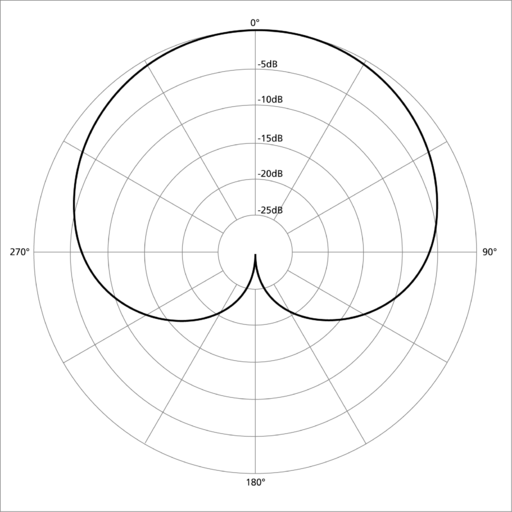
With a heart-shaped pickup pattern, unidirectional mics capture the sound from the top of the microphone and reject surrounding noises. Also, these mics are called cardioid microphones because of the specific pick pattern and must be pointed at the source.
The microphone captures high-directional sounds during recording, but the distance between the mic and the source must be adequate. So, a professional operator needs to maintain a specific length and point the mic to the sound source.
- These microphones are perfect for films, singing, and voiceover work where a specific sound source is necessary. A unique polar pattern isolates the noise from the diaphragm without losing quality.
- The mics’ unidirectional pickup range is greater than the omnidirectional and is used for capturing noise from a specific angle. The unidirectional microphones are challenging to work with because of their sensitivity to a single direction and the experience required to work with them.
Pros:
- Perfect for specific sound isolation
- Highly-directional
- Better proximity effect
- Avoids sound leakage
Cons:
- Effect of wind noise and distortions
- More prone to handling noises
- Not ideal for multi-direction recordings
The difference between the Unidirectional and Omnidirectional microphones
All microphones use the same principle of converting sound waves to electrical signals. However, mics are differentiated according to their unique characteristics of capturing the sounds and their efficiency. So, there are distinctive differences between omnidirectional and unidirectional in how they respond to sounds.
| Polar Patterns | Unidirectional | Omnidirectional |
| Channel Separation | Good | Diffuse field: Less precise |
| Proximity Effect | Yes | No |
| Angle Coverage | 105⁰ to 130⁰ | 360⁰ |
| Maximum Angle Rejection | 180⁰ | No angle rejection |
| Ambient sound sensitivity | 25-33% | 100% |
| Wind sensitivity | Higher | Low |
| Distortions | Higher | Low |
| Gain to feedback ratio. | High ratio | Lower ratio |
| Off-axis coloration | Smooth | Less smooth |
Directionality
- Unidirectional
The high-directional microphones capture sounds from a single direction depending on the positioning of the mic head. It will pick up signals from a specific angle while rejecting the surrounding noises.
The unidirectional mics are cardioid or super-cardioid, depending on the type you are using. These microphones allow the separation of different frequencies, but it is necessary to be careful during positioning.
- Omnidirectional
The omnidirectional mics’ have unique sensitivity, diversity, and reliability in capturing sounds from all directions. During the meetings and group discussions, the mic can record all sources with perfect audio quality.
So, these mics are sensitive to all directions and can be positioned anywhere without worrying about the quality.
Noise Cancellation
- Unidirectional
The microphones are designed to pick up noise from specific sound sources and eliminate surrounding noises. The mics with super-cardioid and hyper-cardioid patterns have built-in filters to reject unwanted frequencies.
Their design and narrow pickup angle make them unique in capturing sounds better than omnidirectional mics.
- Omnidirectional
Their higher sensitivity enables them to capture sounds from every direction and cannot cancel the background interferences. With this, the microphone is less effective in canceling the surrounding noises. So, these mics efficiently work in close environments with required background sounds.
Frequency Response
- Unidirectional
Frequency response is the range of frequencies from low to high a microphone can pick up. Unidirectional mics have specific capturing angles and a narrow frequency pickup response.
- Omnidirectional
Comparatively, omnidirectional microphones have a broader frequency response than the unidirectional mics. It means the mic can carry more frequencies and is perfect for better-quality results.
However, both mics are preferred and found for capturing low-frequency guitars and kick drums.
Polar Pattern
- Unidirectional
Their three main polar patterns, cardioid, super cardioid, and hyper-cardioid, help pick up sound from specific sources. The cardioid refers to the heart-shaped pattern the mic makes during the pickup of sounds.
These mics are susceptible at the desired angle and less sensitive to the opposite directions. However, the sound source must be in the center axis for efficient pickup, or it will produce distorted recordings.
- Omnidirectional
It’s the ideal studio recording microphone with a 360⁰ radius of polar pattern and is designed to capture every detail. In closed environments, the mic picks up surrounding noises with great precision.
However, the zero rejection technology of omnidirectional is not perfect for vocal recordings because it captures unwanted noises.
Leakage
- Unidirectional
Generally, leakage is overlapping one instrument’s sounds into another device. The unidirectional microphones are great because they allow the isolation of the sounds without overlapping surrounding sounds. The mic provides the ideal solutions over leakage, making them the perfect choice for crisp recordings.
- Omnidirectional
Regarding leakage, omnidirectional mics are not the better choice because of the overlapping sounds. The microphone cannot distinguish between desired and surrounding noises during outdoor recordings.
Channel Separation
- Unidirectional
The unidirectional has the unique capability of separating the sound into different channels because it captures from a specific source.
- Omnidirectional
These microphones have less precise channel isolation because they pick up sounds from every direction. However, the ratio between the indirect and direct sounds will never remain intact during the channel separation. So, the mics produce equal gain recordings, which reduce their accuracy in separating the channels.
Proximity Effect
- Unidirectional
The proximity effect increases low-frequency response as the microphone moves closer to the sound source. The proximity actively affects the unidirectional mics because they pick sounds from specific angles. Also, a uniform distance from the start is mandatory, and a slight change can affect the sound quality.
- Omnidirectional
The proximity less impacts the omnidirectional mics because they are designed to pick up sound from every direction. These mics cannot emphasize the low frequencies, so they are not used for live productions.
Distortions
- Unidirectional
Because of the mics’ high directionality and specific pickup patterns, they are vulnerable to distortions. An experienced operator needed to capture the sound source precisely, but a slight change provides distorted recordings.
- Omnidirectional
With fewer to no distortions, omni microphones are excellent because they capture quality sounds from all directions. They are sensitive enough to capture signals and ensure they remain intact without losing their quality.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the unidirectional microphone?
Advantages of unidirectional mic
Unidirectional microphones are exceptional in capturing sounds from a particular source and rejecting the surrounding noises. The mics provide solutions to record crisp, clear audio with precision and focus on ensuring quality. Besides this, there are multiple benefits of using the unidirectional microphones:
Noise Cancellation
Unidirectional is ideal for rejecting sounds in noisy environments because of its narrow pickup angle. The background or interfering noises are called off-axis sounds, ensuring better control over them by focusing on the target source.
Perfect signal-to-noise ratio
Generally, the signal-to-noise ratio is the ratio of the power of signals to the noise, and the mic has better SNR than omnidirectional microphones. The unidirectional picks the desired signals with precision and avoids noise interference.
Versatility
The variety of polar patterns, such as cardioid, super cardioid, and hyper-cardioid, enables a versatile unidirectional mic. Because of this, the microphone is perfect for recording vocals to instruments during recordings or live events.
Focused Sound
The mic focuses on the sound source with a narrow pickup angle and is less sensitive from the rear ends. The unidirectional captures direct sounds and rejects surrounding or reflected audio, so it maintains the quality of recordings.
Disadvantages
Besides the significant advantages, it’s better to understand the attached drawbacks before using the microphone.
Limited Pickup angle
The microphone’s specific pickup angle is its limitation when recording interviews or group conversations. With limited coverage, it picks specific sounds and needs additional mic setups to capture sound from all directions.
Less natural
The microphone records sound from a specific source, which makes recordings less natural because of no ambient noise. When the microphone captures a little noise, it makes it more appealing and removes the artificial nature of the mic.
Sensitivity to handling noises
With high sensitivity, the unidirectional microphones are also sensitive to handling noises. So, moving the mic during the interviews may record unwanted noises and disrupt the overall quality.
Expensive
For professional recordings, the unidirectional microphone uses complex designs for complex recordings. Along with intricate designs, an operator is required for smooth functioning, which makes this mic more expensive. So, these expensive microphones are only used by experts to avoid errors.
Besides the unidirectional microphone drawbacks, they still provide excellent recordings and reject noises efficiently.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the omnidirectional microphone?
Advantages
The ideal microphone for capturing natural sound eliminates the need for a specific sound source. After placing outside the critical distance, omnidirectional provides a variety of advantages over other microphones.
Less wind noise
Like unidirectional mics, the rear acoustic ports are openings where winds can enter and cause turbulence. However, omnidirectional has no rear ports and is unaffected by the wind noise.
Uniform pickup pattern
It eliminates the need to aim the microphone toward the sound source with its uniform pickup angle. The microphone can be placed anywhere, and it will pick up crystal-clear audio with its higher sensitivity.
Reduced handling noise
Omnidirectional mics are less prone to handling issues because they capture sounds from all directions. Also, most handling noises and vibrations result from the proximity effect, and these microphones have no proximity.
In addition, the mics are free to go upside down or right side up, and it will capture all directions without affecting its quality.
No Proximity Effect
There will be no proximity effect because it’s the characteristic of unidirectional mics because of their rear ports. Zero proximity ensures a smooth frequency response regardless of the microphone’s distance from the sources. So, omnidirectional is superior and further ensures quality by rejecting unwanted vibrations.
Disadvantages
Although omnidirectional is ideal for picking up sounds from all directions, it has certain limitations. Therefore, hereunder discussed the drawbacks in complete detail:
Uncontrollable feedback
During live performances, omnidirectional is more prone to feedback because it captures sounds from all directions. So, it picks up the speakers’ sound and amplifies the audio, which will degrade the uniform listening experience.
As it picks up sounds from every direction, it becomes more susceptible to overlapping instruments’ voices. With many bleeds, focusing on a specific sound source will become impossible.
No channel isolation
If you want to remove the noise or specific sound source, then omnidirectional is not a better choice. It is because it captures sounds from every direction with equal gains, which makes it difficult to separate the channels. However, removing the specific sound will affect the indirect-to-direct ratio.
Less noise rejection
Because the microphone captures sounds from all directions, it picks up surrounding noises equally. With this, the omnidirectional is unsuitable for work in noisy environments because of its limited focus.
When to use the unidirectional microphone?
The unidirectional microphones are ideal for live events because they pick up sounds from the source and reject unwanted noises. The mic is the perfect choice for outside recordings, efficiently limiting the background interferences. With this, unidirectional microphones are ideal for use in the following applications:
- Live performances
The sensitivity of unidirectional microphones ensures seamless live recordings of instruments and vocals with minimum feedback. The mic has a strict pickup angle because it captures sound from a single source, so stage noises do not affect it.
- Podcasting
For professionals, unidirectional is ideal with a unique polar pattern and provides crisp, clear recordings with low noise levels. Also, by mounting on stands, the handling noises will be removed, making them perfect for home studios.
- Interviews
The microphone is perfect for conducting interviews during an event to reduce the impact of background noises.
- Recording of studio instruments
The mic will capture recordings without bleeds by mounting the individual unidirectional microphone to studio instruments. However, adjusting the pickup angle is necessary to record crisp, clear recordings without errors.
Along with capturing the recordings of static subjects, focusing on the source from a distance with active noise cancellation is optimal. The unidirectional is the industry standard because it is widely used for films and drama productions.
When to use the omnidirectional microphone?
With little ambient sounds to alleviate the recordings, the omnidirectional is the perfect choice to capture the vocals from all directions. So, the microphone is exceptional to use in the following:
- Stereo recording
During the stereo recording setups, the microphone captures immersive and balanced recordings. Also, its versatility allows capturing multiple sound sources without issues, regardless of their distance.
- Recording a moving subject
Omnidirectional’s distinguishing and unique characteristic is recording crisp audio of the moving subjects. Because of this universality, the mic is used for environmental noises and field recordings, such as sports broadcasting.
Also, during the concert hall recordings, it captures every little detail of the acoustics, making them look more natural.
- Wide sound source
The microphone’s versatility and diversity is the reason for the omnidirectional broader sound source. It is perfect for recording outdoor or indoor recordings from every direction, creating an immersive experience.
- Podcasting
It eliminates the need for pointing the microphone at a specific sound source during podcasting. The mic can be placed anywhere during the recording, creating crisp audio without distortions.
The omnidirectional microphone is essential for reporters to transmit seamless audio during live reporting. However, omnidirectional microphones are comparatively less expensive, and it’s best to check all the parameters before using the mic.
Conclusion
The choice between the audio recordings is not a matter of preference but a decision to elevate the quality of your recordings. Therefore, both microphones have distinct advantages, and selecting the best depends entirely on specific needs.
Also, the requirements and unique goals of the project are essential in developing the choice for the required microphone. For professionals, unidirectional mics can handle complex tasks effectively with unique polar patterns.
So, after analyzing the differences, it’s essential that the mic ensures creativity and will capture detailed recordings without interference.
When deciding between unidirectional and omnidirectional microphones, clarity of voice and freedom of movement are key considerations. A wireless lavalier microphone provides flexibility and reliable audio quality, making it an excellent choice for capturing clear speech in diverse production scenarios.






























.png)