Many people aren’t sure what is audio loopback and how it is used in the audio world. The newcomers stepping into the field of podcasting, music, or audio engineering must have knowledge about it. But unfortunately, not enough information is available even on some of the most popular blogs and sites.
So, in this article, you will learn the meaning of audio loopback. Moreover, you will understand its working methodologies. Additionally, you will also explore its uses and how to set it up. And lastly, there are solutions discussed to overcome common issues in the audio loopback.
So let’s get started.
What is Audio Loopback?
Audio loopback is also called as audio feedback or audio routing. However, these are uncommon names to refer to. Audio loopback is a process of recording, seizing audio from a single source, and then averting it to another source, usually in real-time.
This redirection gives rise to a loop in which audio is ceaselessly passed from one source to another. This results in different processing, monitoring, and effects possibilities. The main idea of an audio loopback is to enable users to control and manipulate audio signals for various applications.
Working Principles of Audio Loopback
Since audio loopback is a method that permits audio signals to be deflected from one source to another, it does create a solid feedback loop. The main aim of audio loopback is to allow audio monitoring, recording, routing, and sound manipulation.
This entire process can be applied using various techniques with the help of software and hardware programs, depending on your requirements and availability of equipment.
1. Audio Loopback using Software
Audio loopback is possible using a wide range of software programs, such as:
a. Tools in the Operating Systems
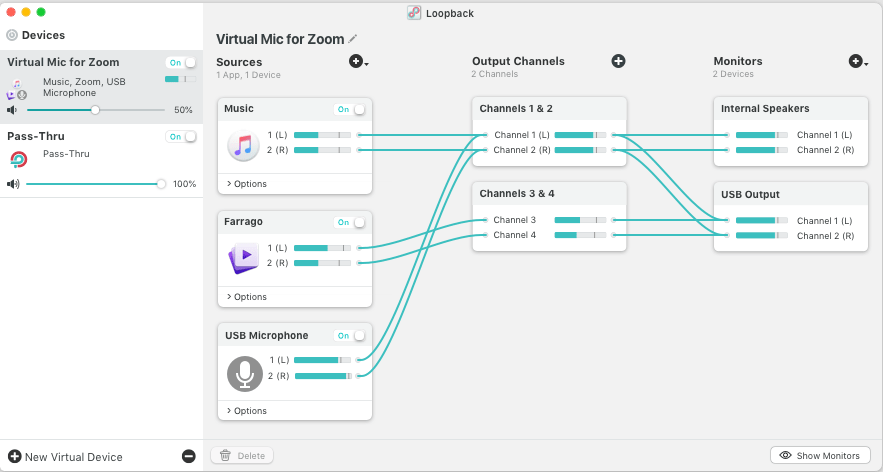
Not all, but some renowned operating systems offer incorporated routing tools that help configure audio loopbacks. Linux and Mac (some OS versions) are famous for providing such facilities for audio engineers and music producers. These tools are helpful when it comes to redirecting audio from different applications.
For example, through audio loopback operating systems, you can route audio from your web browser to a DAW. Likewise, you can send audio from any media player to a voice chat application.
b. Effects and Plugins
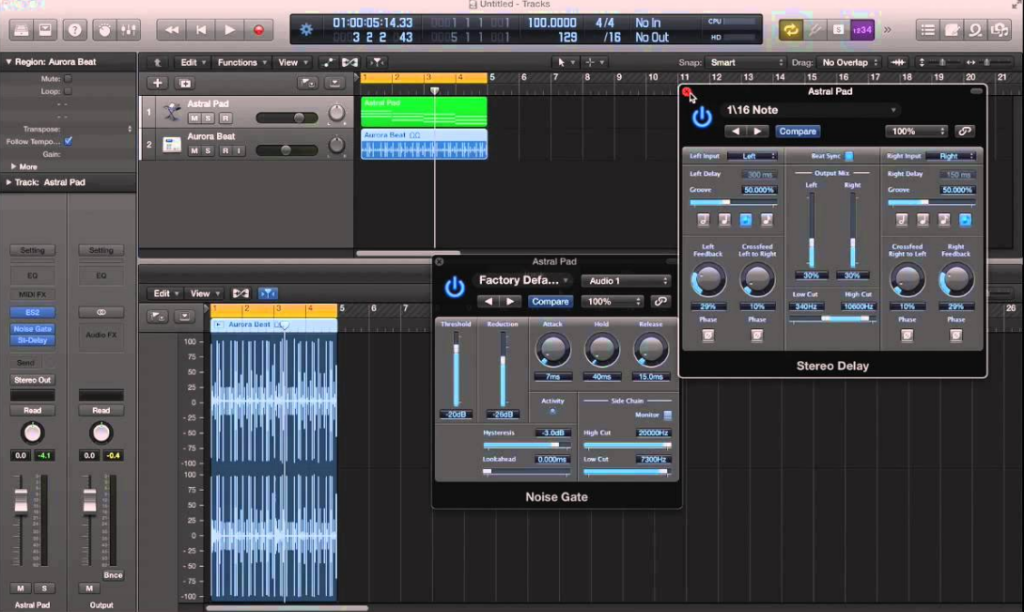
Audio effects and plugins in DAWs are also valuable tools for developing audio loopbacks. By applying effects to your audio signals and then redirecting the output, you can accomplish creative and unique sound. This is a very common practice in digital music production, where musicians aim to create different sounds.
c. Audio Stream Input and Output Drivers (ASIO Drivers)

While professionals typically use the ASIO drivers to achieve low latency during audio processing, these programs also come with audio loopback functions. This allows smooth audio routing between hardware and software.
d. Virtual Audio Cables (VAC)
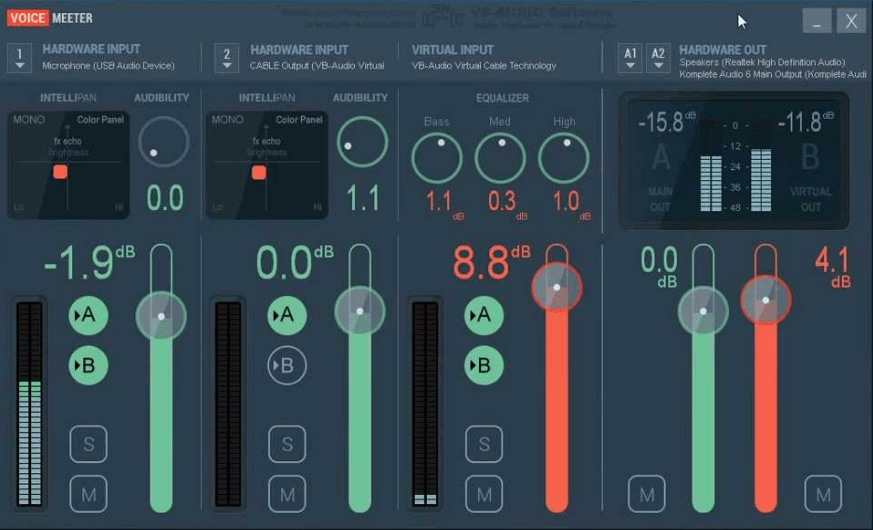
A virtual audio cable is a software application that creates virtual routing for the audio signals. This application is employed in computer-based sound setups. It allows you to redirect audio between different devices and software. Virtual audio cables are also useful for functions like audio streaming between multiple applications or recording the audio output of a particular application as the input for another application.
e. Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
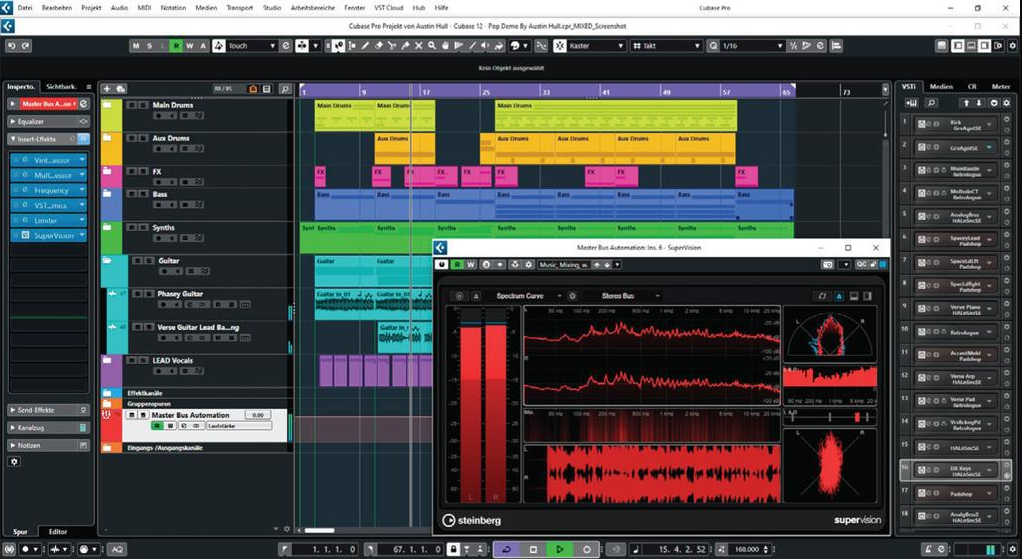
Popular DAWs like Steinberg Cubase, Logic Pro, and Acid Pro provide built-in audio loopback features. In digital audio workstations, you can redirect audio tracks to various destinations to create a variety of feedback loops and processing chains. This is really helpful in the music production field, as it permits music producers to implement different signal processing and effects to their tracks.
2. Audio Loopback using Hardware
There are many great hardware tools you can use to achieve audio loopback, such as:
a. Audio Interfaces

There are many audio interfaces that have the capability to perform audio loopback, as they are equipped with the right hardware. Such interfaces allow direct audio routing from a given input to an output source within the system. It means you don’t have to use any other devices with your audio interface to savor audio loopback.
This trait is extremely beneficial for functions like recording and monitoring. For example, it enables audio engineers and musicians to listen to what they are recording or playing in real-time without delay. That is one of the reasons why audio interfaces are essential gadgets in music production.
b. Digital Audio Processors

Hardware devices like digital audio processors also have audio loopback as one of their main features. But unlike audio interfaces, you need to integrate these processors into your established audio setups to improve audio processing. For instance, you can use a digital audio processor to apply effects to a specific audio signal and redirect the processed audio into the system for additional manipulation.
c. Mixers

If you have a professional audio mixer, it will surely provide you with dedicated channels for audio loopback purposes. These mixers allow you to route sound from different sources, including instruments, microphones, and other external gears, building robust audio signal paths. This feature is great for mixing music, whether live or studio-based.
3. Audio Loopback using Software and Hardware Together
There are times when software and hardware tools are used together to get the required audio loopback. For example, sound engineers may use a virtual audio cable to route audio from software to a digital effects processor. Next, the processed audio signal can be redirected back to a DAW for extra manipulation. This hybrid methodology permits immense customization and flexibility in the overall audio processing.
Uses of Audio Loopback
Audio loopback is used in different industries, such as:
1. Sound Testing

“1, 2, 3 mic testing” – You may have heard this before the event starts. Likewise, a sound check happens before beginning the concert. These actions are taken just to make sure there is no signal loss in the audio in terms of quality. But what is the thing that ensures audio technicians and engineers that the audio is top-notch? It is the audio loopback that they employ for testing audio equipment, including amplifiers, speakers, and microphones.
By looping signals through different audio components, they can evaluate the fidelity, response, and quality of the equipment. Loopback analysis also helps determine and understand problems like distortion and latency, ensuring that your audio equipment is set according to performance standards.
2. Live Streaming

YouTube, Facebook, YouTube, or any other renowned live streaming platform excessively rely on audio loopback. Streamers use this technique to combine different audio sources without a hitch. For instance, they can merge music playlists, microphone input, and chat conversation into a single combined stream.
So, to make that happen, you need audio routing from different sources into your broadcasting software, mostly with the help of software-based loopback. Therefore, audio loopback ensures that your audience (listeners and viewers) experience well-organized and seamless audio and visuals simultaneously.
3. Podcasting

Podcast artists continuously use audio loopback to supervise their recordings to ensure everything goes smoothly. Through audio loopback, they can hear their guests’ voice and their own vocals along with background music or sound effects in real time. This real-time supervision is vital for maintaining engaging and high-quality conversation to ensure impeccable audio quality. Therefore, audio loopback improves the overall quality of the podcast.
4. Audio Recording and Mix

When it comes to audio engineering and music production, audio loopback is a method that cannot be avoided. In fact, it is widely used in recording and mixing. Audio loopback permits your recording software to capture software-generated sounds, like synthesizers and virtual instruments.
Most importantly, audio loopback allows you to record multi-track where each vocal track and instrument can be recorded individually within the digital processing workstation. These individual tracks can later be used to create an entire song. This is extremely necessary for attaining the desired sound quality and producing high-quality, professional-standard music.
5. Gameplay Audio

The modern way of gaming, where streaming can help you earn good money, was impossible without audio loopback. Why so? Because audio loopback enables gaming streamers to add flavors to their content. It permits them to capture the gameplay audio, as well as the narration or commentary they do to share the experience with their audience.
6. Assistive Devices
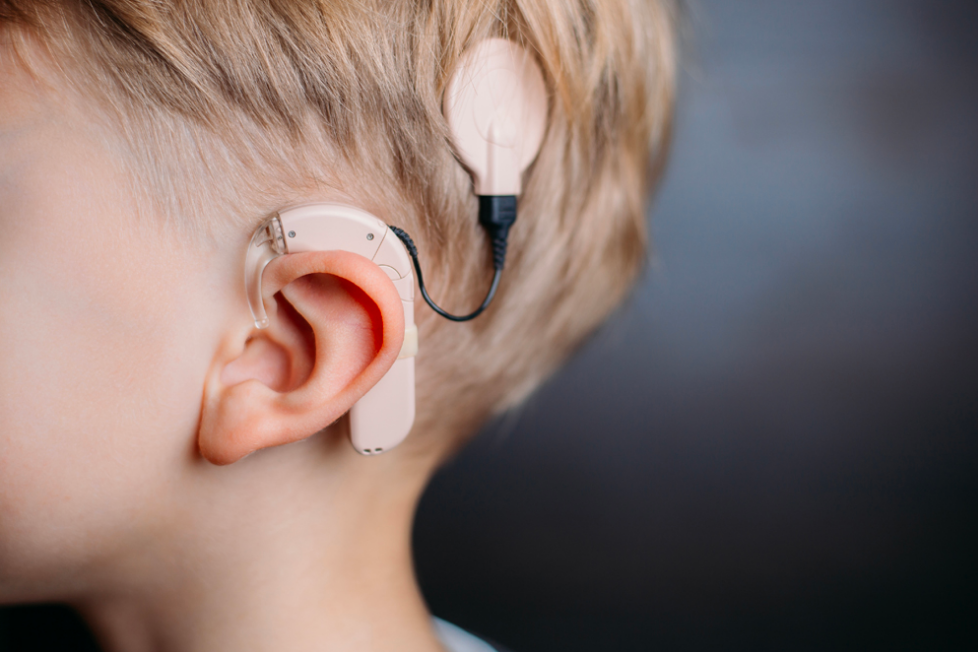
Audio loopback not only serves the music and gaming industry, but it is also a boon for people with hearing impairments. This technology permits audio from a mic to be played via hearing aids or headphones, offering real-time auditory experience and feedback. This is excessively useful for individuals who use hearing devices, such as cochlear implants, as it lets them interact and communicate with other people.
How to Install and Setup Audio Loopback? Software vs Hardware
In this section, you will learn ways to set up audio loopback when using software or hardware programs.
How to Install Hardware Audio Loopback?
- Step 1: Connect your audio sources, such as a computer, instrument, or mixer, to the out of the audio interface using TRS, XLR, or RCA cable.
- Step 2: Next, connect the input of your audio interface to your processing or recording device, such as DAW.
- Step 3: Use your audio interface’s routing option to configure audio loopback. Make sure that there is a balanced loopback signal.
- Step 4: Correctly adjust the output and input levels on your audio interface to get the desired sound quality. However, ensure all levels are set in a way that there is no noise, distortion, or feedback in the audio.
How to Setup Software Audio Loopback
- Step 1: Install any virtual audio cable software, such as BlackHole or Voicemeeter, on your computer.
- Step 2: Create different virtual audio devices within the software. Creating these devices will work as intermediaries for audio routing between the system and software.
- Step 3: Configure the audio software to the virtual audio device output you created in the first step. This step is necessary for averting the audio flow.
- Step 4: In your DAW, make sure to set your virtual audio device as the main input source to let your software receive audio signals from the virtual device.
- Step 5: Adjust volume levels appropriately to avoid distortion and begin recording.
Solutions to Common Issues in the Audio Loopback with Possible Fixes
Although audio loopback has a wide range of uses and its setup is also easy, there are some issues that users face. Here, you will find the most common problems encountered in audio loopback with ways to fix them.
a. Feedback Problem
Echo and feedback happen when your audio loopback’s audio output creates a constant loop, which sometimes results in unwanted sound.
How to Fix Feedback in Audio Loopback?
Make sure your output and input levels are correctly balanced on your audio interface. Moreover, use in-ear monitors or headphones to isolate the audio loopback from your speakers or studio monitors.
b. Latency Problem
Latency is one of the most common problems in audio loopback. It means the delay of signals between audio input and output. This issue can lead to various audio synchronization problems, especially during live environments, such as streaming.
How to Fix Latency in Audio Loopback?
If you are using hardware audio loopback, then purchase a better audio interface and high-quality cables. In a software-based audio loopback, adjust the size of the buffer in your streaming or recording software to reduce latency. You can also use ASIO drivers for this purpose.
c. Bad Audio Quality
Most users with software audio loopback complain about low audio quality, causing lower fidelity.
How to Fix Bad Audio Quality in Audio Loopback?
Download excellent and tested virtual quality cable recommended by the experts. Adjust the bit depth and sample rate in your software to enhance audio quality.
Conclusion
The simplest explanation of what is audio loopback is the technique of recording different sound sources simultaneously using hardware or software programs. You can use virtual cables, DAWs, ASIO, and various plugins to create audio loopback using software. Contrarily, you need to invest in equipment like mixers, digital audio processors, and audio interfaces to get audio loopback using hardware.
Audio loopback is used in numerous ways, such as for audio recording and mixing, live streaming, gameplay audio sharing, assistive devices, and sound testing. Moreover, the process of setting up and fixing audio loopback issues is pretty straightforward.
When troubleshooting audio loopback, clear sound input is crucial to prevent unwanted noise or distortion. A reliable wireless lavalier microphone can significantly improve audio clarity and reduce loopback-related issues at their source.
FAQs
Q1. What is audio loopback good for?
Audio loopback redirects audio from your studio monitors or headphones into another application for recording or streaming without losing fidelity.
Q2. What is audio loopback test?
The audio loopback test ensures that the audio signals are redirected perfectly.
Q3. Is audio loopback free?
Some software programs, such as Rogue Amoeba, are free to download for audio loopback.
Q4. Which audio interfaces have audio loopback?
Many audio interfaces come with an audio loopback functionality, such as Focusrite Scarlett 4i4, MOTU M2, and Universal Audio Apollo Twin X DUO.






























.png)





