Filters are important in signal processing, allowing you to shape and control sound and other electrical components by manipulating electronic signals. While there are several types of filters, the low-pass filter keeps its own value in a variety of applications. Nevertheless, when it comes to sound mixing, low-pass filters give you the power and impact over the feel and tone of the mix.
This article tells you what a low pass filter do by defining it and showing you how it works. Moreover, you will learn 5 ways to use a low-pass filter. Besides, you will also explore its applications in different fields.
What is a Low-Pass Filter?
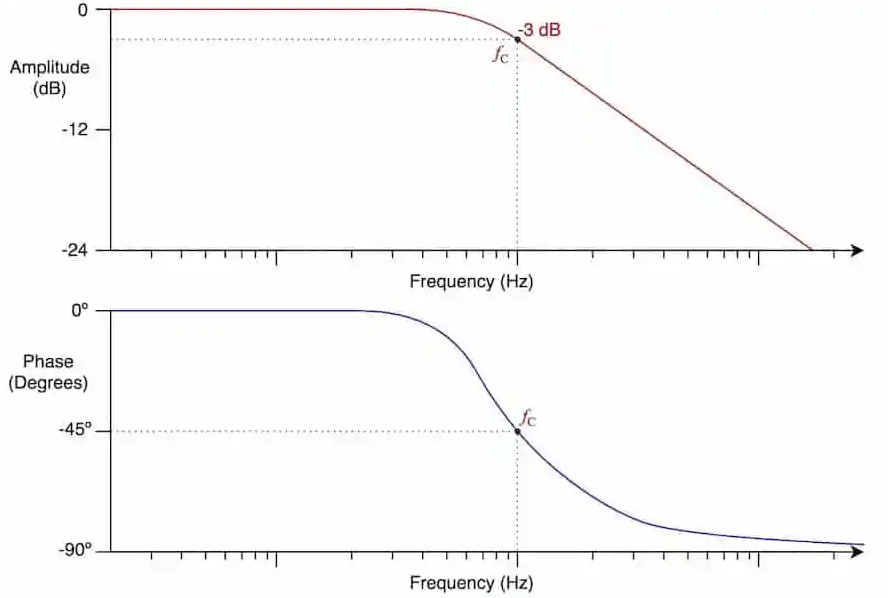
A low-pass filter (LPF) is an electronic circuit that permits low-frequency signals compared to their cutoff frequency to travel through while barricading high-frequency signals. In other words, it allows low-frequency components of any signal to pass side-by-side, eliminating or reducing high-frequency components. The main reason to apply a low-pass filter is to limit or smooth the continuous amendments in a signal. This allows to experience more predictable and managed output signals.
How Does a Low-Pass Filter Work?
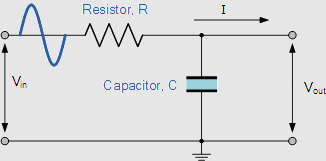
Low-pass filters function using the frequency selectivity principles. They use a blend of inductors, capacitors, and resistors to build a frequency-dependent response. The main element in a low-pass filter is its capacitor, which obstructs the stream of high-frequency signals, permitting low-frequency signals to easily pass through.
The basic circuit of a low-pass filter comprises a capacitor (denoted by C) and a resistor (denoted by R), which are connected to each other in series. At the same time, the output is gathered from the joint between these two components. This formation makes a simple resistor-capacitor (RC) low-pass filter. This filter’s cutoff frequency (fc) is an essential parameter and is identified through the values of the capacitor and resistor.
When the input signal frequency increases, the capacitor reactance decreases, permitting more signals to pass by. Contrarily, the reactance of the capacitor grows on all the frequencies under the cutoff frequency. This leads to significant blockage of high-pitched signals.
5 Ways to Use Low-Pass Filter in Audio
Now that you know what does a low-pass filter do? Let’s learn its uses in the world of audio.
1. Adding Depth to Audio
Mixing engineers strive to create a mix with depth. This means that the song includes a feeling of physical distance in the back and front of the soundstage. To understand this point, think of how you perceive sounds regularly – the further the sound source is from you, the less you can hear it. The same happens when you try to listen to your voice when speaking nearby by traffic. The sound of horns and vehicles blends with your voice and gives you difficulty hearing your own sound.
A similar approach is used when walking inside the studio and mixing audio tracks. Some audio signal frequencies overshadow others, which is why applying a low-pass filter helps you diminish high-frequencies from the sound.
2. Removing Unwanted Frequencies
Low-pass filters are excellent tools for dealing with high frequencies that create problems, such as hiss in a noisy audio recording, undesirable resonance from poorly microphoned guitars, and more. These types of grungy and unwanted degradations may not be noticeable during the recording process. However, they make a lot of mess in the mixing and mastering phases.
3. Decreasing Frequency Masking
Many times, instruments clash during recording and mixing. For instance, an acoustic guitar and drum kit serves different functions. But they do clash with one another in the treble range, especially when the guitarist strums aggressively. This kind of playing conflicts with the cymbals and hi-hat of the drums. In this scenario, audio engineers utilize low-pass filters to distance one instrument from another. So that the audio track sounds clean.
4. Adding Variations to the Same Sound
A low-pass filter helps you create different versions of the same sound. For instance, you have two pieces of instruments in your audio track. The second piece is a copy of the first. So, in order to make the second piece different and spicy, you can apply a low-pass filter to enhance the music arrangement,
5. Defining a Point in Your Sound
Last but not least, sometimes, you need to bring certain sounds up while reducing other sounds to become more hearable and better defined. For this purpose, a low-pass filter is also used to add a high-end cut and resonance.
Other Areas where a Low-Pass Filter is Applied
Although low-pass filters are widely used for audio engineering and music production, they also play a key role in other fields, such as:
a. Image Processing

Low-pass filters are also used in the image processing. They help blur and smooth visuals, preventing noise and improving the overall image quality. The Gaussian filter is one of the best examples of low-pass filters in image processing.
b. Communication
Regarding telecommunication, experts implement low-pass filters to restrict the signal bandwidth to prevent high-frequency elements from interfering. This is necessary for controlling signal integrity and diminishing data corruption chances in communication systems.
c. Biomedical
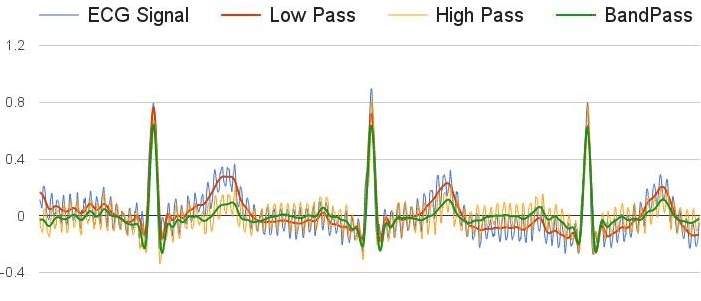
In the field of biomedical signal processing, such as EEG and ECG, low-pass filters are used to eliminate high-frequency interference so that the physiological signals are more visible. This helps properly diagnose the patients and further aids in treatment.
Conclusion
Low-pass filters limit high-frequencies from disrupting signals. There are many ways to answer the question, “What does a low pass filter do?” Firstly, these filters are widely used in music production and sound engineering works. They help clean the sound by decreasing high-frequencies from the audio. Secondly, a low-pass filter is applied in various other fields, such as telecommunication, biomedical machinery, and image processing.
When working with audio signals, applying a low-pass filter is crucial for capturing clear vocal recordings without unwanted high-frequency interference. To further enhance sound clarity in video productions, using a reliable wireless lavalier microphone ensures professional-quality audio capture in diverse filming environments.
FAQs
Q1. What is the effect of a low-pass filter on signal?
Low-pass filters help remove noise, clean up signals, and create a soft and smoothing effect.
Q2. What does a low-pass filter get rid of?
A low-pass filter ceases frequencies that are greater than the cutoff frequencies from entering the signals.
Q3 Is the low-pass filter good or bad?
A low-pass filter is necessary for removing high-frequencies. However, the low-pass filtering process is less common compared to high-pass filtering.






























.png)





