When it comes to audio engineering, gain staging holds a vital position for attaining high-quality sound. The term refers to the optimization and strategic management of audio levels at different stages of audio recording to ensure there is no distortion in the audio and there are significant signal-to-noise ratios so that the audio output is well-polished.
So, this article clears the concept of what is gain staging and how it works on analog and digital platforms. Furthermore, you will also learn the importance of gain staging and its entire process so you can apply the best practices to achieve professional-level audio quality.
What is Gain Staging?
Gain staging is the process that involves keeping the right gain levels on all the stages of the audio signal to maintain a high-level balance between the noise floor and signal strength. Here, the term optimal means loud sound to the inherent recording’s noise floor, but not extremely loud, which causes distortion when the audio goes to the next processor in the chain.
That means gain staging is based on an appropriate gain adjustment to prevent insufficient amplification that causes a low signal-to-noise ratio. At the same time, it means preventing excessive amplification that distorts the audio.
In simple words, gain staging is related to adjusting the knobs of a mixer board or any sound-processing device to make sure that the audio signals are clear throughout the audio production process.
What is Gain Staging in Digital vs Analog?
Digital and analog gain staging are two similar practices at the beginning, but they differ from each other as the process moves into depth. Digital gears have their own limit of 0 dBFS. When an audio signal goes above this level, you can receive hard digital clipping, as seen in the squaring waveform below.
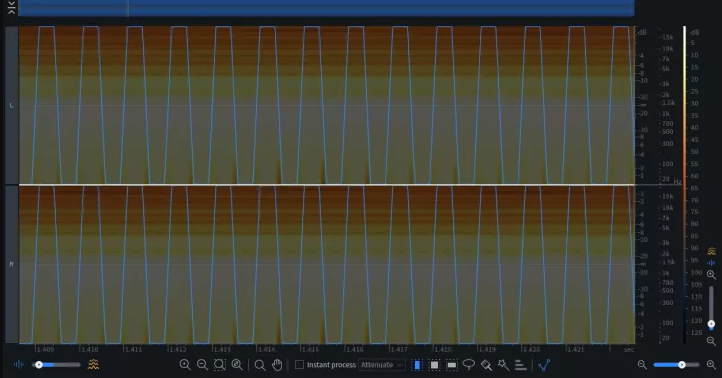
When it comes to audio gears, the limit is higher for distortion. This distortion can sometimes sound good to the ears. Therefore, when setting analog processor levels, you ensure to preserve some room before the audio signals hit distortion.
What is the Importance of Gain Staging?
So you now have a little idea about what is gain staging. Let’s learn how crucial it is in audio engineering from different aspects.
a. Control and Consistency
When you apply an effective gain staging strategy, it permits you to experience controlled and consistent adjustments in the entire signal chain. This facilitates a smooth workflow and allows audio engineers to attain the desired sound frequently across different mixing elements.
b. Effective Processing Power
When audio engineers optimize gain staging, it helps enhance resource efficiency. Optimizing gain ensures that each component functions within the ideal audio range, preventing outrageous amplification.
c. Signal-to-Noise Ratio
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is an important concept in sound engineering and gain staging. It plays a great role in analyzing the overall audio quality of recordings. SNR shows the relationship between the unwanted background interference or noise and the desired audio signal in your recording.
Therefore, maintaining a high SNR is necessary for preserving the quality of audio across the signal chain. When an audio signal goes through different processing stages, including amplifications, effects, and mixing, it is open to accumulating noise. That is why proper gain staging makes sure that your audio signals are louder than the background noise without degrading the sound quality.
At the same time, a high signal-to-noise ratio ensures that the noise floor remains low, permitting the audio signal to show up clearly and prominently. You must also know that inadequate gain staging can cause signal clipping, which results in unwanted noise and distortion. But by maintaining proper SNR, it is easy to avoid audio clipping.
d. Safety from Distortion
When gain staging is improper, the process of administering audio signal levels at each production stage can cause distortion. Distortion is the outcome of excessive amplification of audio signals, which causes an unwanted alteration in the audio waveform. This kind of degradation impacts the overall audio quality, making it important to prevent distortion, especially in a professional environment.
Distorted audio is mostly characterized by unpleasant and harsh sound that comes from the intended source, lessening the accuracy and fidelity of the original audio recording. It can be of any type, including intermodulation distortion, clipping, or harmonic distortion. And each of them can affect the audio differently.
Therefore, effective gain staging is a concept that proposes to set correct levels at each stage of the audio signal path. This ensures that all the signals are within the optimal levels so the distortion can be avoided. Maintaining gain staging is the prerequisite for getting natural and clear sound.
e. Managing Headroom
Headroom means the space between the maximum level of audio without clipping or distortion and the maximum peak of an audio signal. A well-managed headroom permits for managing surprising audio peaks without giving up on the audio quality. So, it is important to adjust gain at all levels to maintain headroom. This is essential in audio production as it ensures undistorted, clean sound throughout the process of audio production.
For example, when you are recording audio, you need to set the correct input levels on the instrument or microphone to make sure the signal doesn’t surpass the highest capacity of the audio equipment. Likewise, during mastering and mixing, you need to adjust the levels properly to maintain a balanced sound and prevent clipping problems.
What is the Gain Staging Process?
Audio engineering is an art, and gain staging plays a key role. Proper gain staging is important to achieve top-notch audio quality, as it ensures that the audio signal travels throughout each audio processing chain with correct amplification and unwanted noise. So, let’s discuss the fundamental process of gain staging.
Stage 1: Keeping the Right Input Gain
The first step to gain staging process is the sound source. Whether you have a microphone that captures the singer’s performance or any instrument as an output, this initial level is fundamental as it keeps the base for the signal path. Here, it is vital to maintain a proper input gain on your recording equipment because the goal is to record not only clean but a strong signal without overburdening the input.
To control the input gain, you usually use a slider or a knob to show the sensitivity of the audio signal. Setting input gain extremely low may produce a noise-prone and weak recording. Whereas setting it extensively high will bring distortion as it pushes the audio signal beyond the recording device’s potential.
Stage 2: Setting Microphone Preamps Correctly
The next goal is to correctly set the mic preamplifiers on your mixers or audio interfaces. However, before you do that, keep in mind that the main aim of a microphone preamp is to augment the weakest microphone signal following the line level so you can further process it. During this stage, it is necessary to adjust your preamp gain systematically to attain a good input level without distortion.
This stage comes with a goal that the microphone preamplifier is set in a way that the loudest areas of the sound source do not surpass the coveted recording level. This ensures that all your audio signals remain distortion-free and clean in the overall recording process.
Stage 3: Apply Effects and Processing
The next step in the gain staging process involves implementing different effects and processing the audio signal. This includes reverb, compression, equalization, or other effects that carve the sound to meet desired technical or artistic requirements. But, again, this stage requires maintaining a balance in the signal level.
That means you must make sure that the output and input levels are adjusted correctly. For example, if you are applying a compressor effect, you must set the input level in a way that matches the incoming audio signal, as well as the output level, to attain the correct amount of compression. Failure to do so may cause inconsistent levels and destroy the audio quality.
Stage 4: Correct Gain Level Adjustment on Your Mixer
These days, there are multi-channel audio setups like mixing consoles, where each channel has its own gain control, referred to as trim controls or channel faders, permitting you to adjust the input level for individual channels. This means you need to properly set the gain for every channel to enjoy a balanced mix.
Balance mixing is important, as it ensures that all your audio elements work harmoniously. If channel ‘A’ has a higher gain than channel ‘B’ or ‘C,’ it will oppress the mix, making it difficult to apply other effects. Moreover, higher levels of this will also cause distortion.
Stage 5: Fine Adjustments to the Master Fader
The last stage of gain staging happens at the master fader. It controls the entire output level of your mix. Therefore, adjusting it properly is necessary to make sure the mix has a suitable level for playback or recording without distortion. This is the place where you can fine-tune the mixing levels. So, if your mix is too soft or loud, use this control to balance levels.
Tips for Successful Gain Staging
Since now you have an understanding of what is gain staging and the entire process, let’s learn the best practices for fruitful gain staging so you get a clean audio recording.
a. Increase Gain Gradually
The best way to achieve gain staging is to take things slowly. Remember, excessive amplification leads to distortion, which is pretty tough to correct later. So, it is comparatively easier to increase gain levels little by little to save yourself from overdoing the process for the sake of rectification. This approach mitigates the risks of unwanted noises in your audio.
b. Make Use of Visual Indicators
Some of the best visual indicators, like peak or VU meters, are irreplaceable tools for observing input and output levels. As an audio engineer, you should regularly review these meters to make sure that all the levels are in the correct range. Overloading the audio signal with loud volume can surely cause distortion, and you lose audio quality. But, by using these devices, you can easily maintain the best signal.
c. Maintain Adequate Headroom
You cannot deny the fact that maintaining sufficient headroom in the signal chain is vital, especially in the master fader and preamp stage (discussed in the previous section). Try to keep the headroom between the ranges of 6 dB and 12 dB to overcome unexpected audio peaks leading to distortion in the audio.
If you look at the screenshot below, you will see that the first bar represents a sine wave with adequate headroom. The second bar shows less headroom. The third bar shows that the audio is clipping since there is no headroom. Your goal is to maintain plenty headroom to avoid distortion or clipping.

d. Evaluate Phase and Polarity
Phase and polarity are two major problems that cancel audio signals or cause phase-related issues. Both of them must stay consistent across all audio channels. This will help you stick to optimal audio without causing phase and polarity problems.
e. Keep Continous Monitoring
To make the gain staging process win, you must keep your eyes on the production process. Indulge in continuous monitoring and be regular when it comes to adjustments so the audio levels remain distortion-free and balanced.
f. Don’t Forget to Document the Process
Lastly, regular documentation is an integral part of the gain staging process. You must habitually document gain settings for each stage in the signal chain, especially if you are dealing with complex projects. This practice will save you time and effort for future tasks. Moreover, you will be able to keep up with the consistency throughout different mixing and recording sessions.
Conclusion
What is gain staging? The easiest explanation is that it is a process in audio recording to keep vocals or instruments sound clean without distortion or clipping. It is a crucial process that helps you maintain enough headroom so that the audio waves are in their correct form. However, to ensure you perform the right gain staging, you must increase gain slowly, use visual meters, and monitor the audio file to prevent distortion.
Proper gain staging is crucial to capturing clean audio without distortion or unwanted noise, especially when recording in dynamic, real-world environments. Using a reliable wireless lavalier microphone ensures consistent audio levels, giving you greater flexibility and higher-quality results throughout your production workflow.
Best Seller
Sale
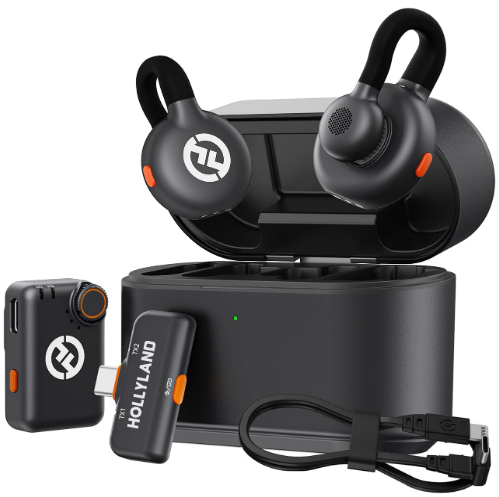

Hollyland LARK M2S – Wireless Clip-on Microphone
- 7g Lightweight, Titanium Clip, Discreet Design
- Clear sound with 24-bit/48kHz, 70dB SNR, 116dB SPL
- Noise Cancellation & 300m Long-Range Stability
- Works with Camera/iPhone/Android/Laptop
- Perfect for Content Creators, Online-Teaching, Streaming
$139
$159
FAQs
Q1. What is the purpose of gain staging?
Gain staging ensures that your audio has minimal chances of getting distortion and noise.
Q2. What is an example of gain staging?
For instance, if you have applied EQ and are willing to apply delay or reverb, then each effect has its own gain stage with input and output levels.
Q3. What is the best level of gain staging?
You should aim for -18 dBFS with a maximum audio peak hitting -10 dBFS. However, it is vital to keep your audio channel at most -6 dBFS.
Q4. What is the difference between gain staging and leveling?
Gain staging organizes audio for the next processing stages. Level is the process that comes after gain staging, where you adjust multiple tracks during the mixing process to avoid additional gain.


























.png)



