In the music world, compression performs a great help in music production to yield the right sound effects. Many professional musicians utilize compression tools to control the dynamic range and achieve better sound effects.
But if you are an aspiring musician and need clarification about what exactly compression does, then here you will get all the answers to your queries. Let’s understand what does a compressor do in music.
What is an Audio Compressor?
Before knowing the importance of compressors, you first need to know what exactly audio compressors are.

The audio compressor is an audio editing tool that is used to manipulate the dynamic range of an audio single. It means an adjustment between the loudest and quietest parts of the audio. Utilizing an audio compressor is considered an essential task for equalization and applying audio effects. The compressor provides multiple controls like threshold, ratio, attack, release, and makeup gain to compress dynamic range to produce natural sound effects. It has become an important tool for mixing any kind of music.
What Does A Compressor Do In Music?
As we already discussed above, what exactly is an audio compressor? And now we will know about the main query: what does a compressor do in music?
The compressor is used to reduce the dynamic range of signals with different parameters. Basically, compression distorts the audio signal and changes the original sound of Singla through processing.
It emphasizes the harmonic based on how the compression hits the incoming signal. Dynamic ranges become narrower, and the difference between the highest and quietest parts has fewer DB levels.
Understand Compression Parameters
To understand what a compressor does in music, you need to understand the various parameters of compression. This audio-enhancing tool provides several controls to get better quality sound.
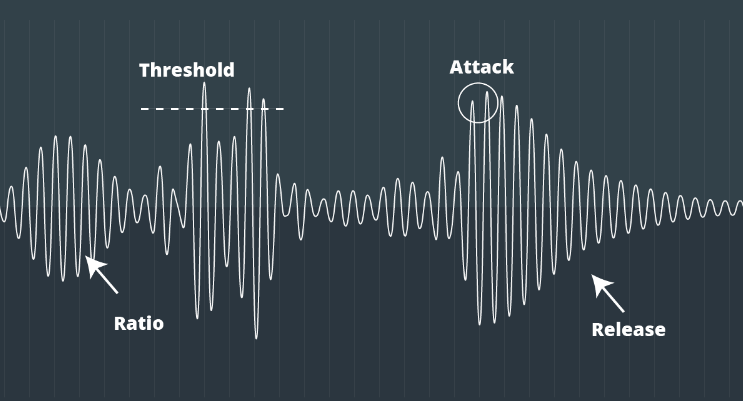
- Threshold
A threshold is the level where the dynamic process starts. which compression begins to act on a signal and is measured in dB. When the audio goes above the threshold level, it triggers compression, and when the audio is below the threshold level, compression does not react.
- Ratio
The amount of compression above the threshold is controlled by the ratio. Higher ratio numbers determine more intense compression. It is expressed as a numerical value, such as 3:1 or 4:1. Ratio represents the relationship between the input signal level and output single level after compression. By adjusting the ratio, you can achieve a polished and professional sound effect.
- Knee
The compression transition from an uncompressed to a compressed state is referred to as the knee. It establishes how the compressor reduces the signal when it reaches a predetermined threshold. A hard knee is a sharp transit that offers more pronounced compression.
- Attack and Release
The attack and release determine the timing of the compression action. This feature do a key control for making compression sound more pleasing. Controlling aggressive transients can be effectively achieved with a swift attack. The compressor’s action may appear more subdued and less dramatic with a gradual release.
When Do You Use an Audio Compressor?
Now that you are familiar with audio compressors, you also need to understand when to use an audio compressor. Take a look at some common scenarios where audio compression can be of great help to you.

- To Reduce Dynamic Range
Audio compression is a very useful tool for live recording; it helps reduce the dynamic range of an input signal. The fully compressed mixes are easier for listeners to digest and make additional frequencies for the mix. The unstable input and output levels can easily be managed with audio compression on a live recording.
- Shaping the Sound
You can use audio compression for fine-tuning or shaping waveforms to ensure consistency. To shape the transients equally, for example, it is very common to compress all drum parts, including the kick, snare, and hi-hats. To keep drum parts from sounding too prominent throughout the mix, they must be rounded off.
- Parallel Compression
Parallel compression is the process of combining an unprocessed signal with a completely compressed signal. This additional level of control generates a distinct sound and can make it simpler for artists to get the desired blend of compression.
- Sidechain Compression
The sidechain compression effect is used to highlight certain instruments over others that are in the same frequency range. For example, the kick drums and bass guitar frequently occupy a large portion of the low-end frequencies when they are playing simultaneously.
Common Errors and Advice
After understanding the importance of compression, you should understand what common mistakes everyone makes while compressing sound. You should be aware of these mistakes and follow the best tips to get the best results.

- Attack too fast on drums
When you first get your hands on a compressor plugin, it can be tempting to hear it clamp down as hard as possible. On the drums, this can be a real problem to mix. The transients will be forced too deeply into the drum’s body to pass through a dense track if the attack is executed too quickly.
As a result, your mix might sound lifeless and flat, and your drums might disappear altogether. Alternatively, to preserve the drum track’s original crack and snap, schedule the compressor’s attack to begin immediately after the first attack.
- Too-low threshold
One may assume that applying more pressure to the threshold will intensify the compression effect. To some extent, it will, but the dynamics involved are a little more involved than that. A significant portion of the character the compressor adds to a sound is hearing its release.
You will not really be able to hear the compressor’s full potential if the threshold is set so low that it never releases. A gain reduction needle that jumps and bounces in time with the beat is often indicative of musical compression.
Conclusion
No doubt, the audio compressor is an essential tool for musicians and sound engineers. But before you use one, it’s important to understand all the audio control features and know how to use them perfectly to gain perfect results. Audio mixing is a critical aspect of music production, and with the right creativity and the right tools, anyone can polish their audio quality.
As you explore compression and its effects on vocal clarity, choosing a reliable microphone is equally vital. A professional wireless lavalier microphone ensures clear, consistent vocals, providing the compression process with high-quality audio input to create polished sound recordings.
FAQs
How does the compressor enhance sound quality?
The audio compressor acts as a balancing tool for audio signals. By boosting the quieter parts and reducing the louder ones, it smooths loudness variations. Musicians used compression to reduce dynamic range and shape the sounds by adjusting parameters.
When should use an audio compressor?
Use the audio compressor whenever you need to reduce the dynamic range of audio signals. A more balanced, consistent sound is produced by dynamic range compression, which reduces the gap between the highest and lowest amplitudes throughout a signal chain.
Does compressed audio sound better?
Yes, compressing the louder audio signals and boosting up the lower signals, improves the overall sound experience. You get more smoother and consistent sound clarity
Does audio compression reduce quality?
Reduces the audio quality for novices who are unfamiliar with compression tools and are unaware of the various compression parameters. To produce better output, you must be familiar with all parts of the compression tool.






























.png)