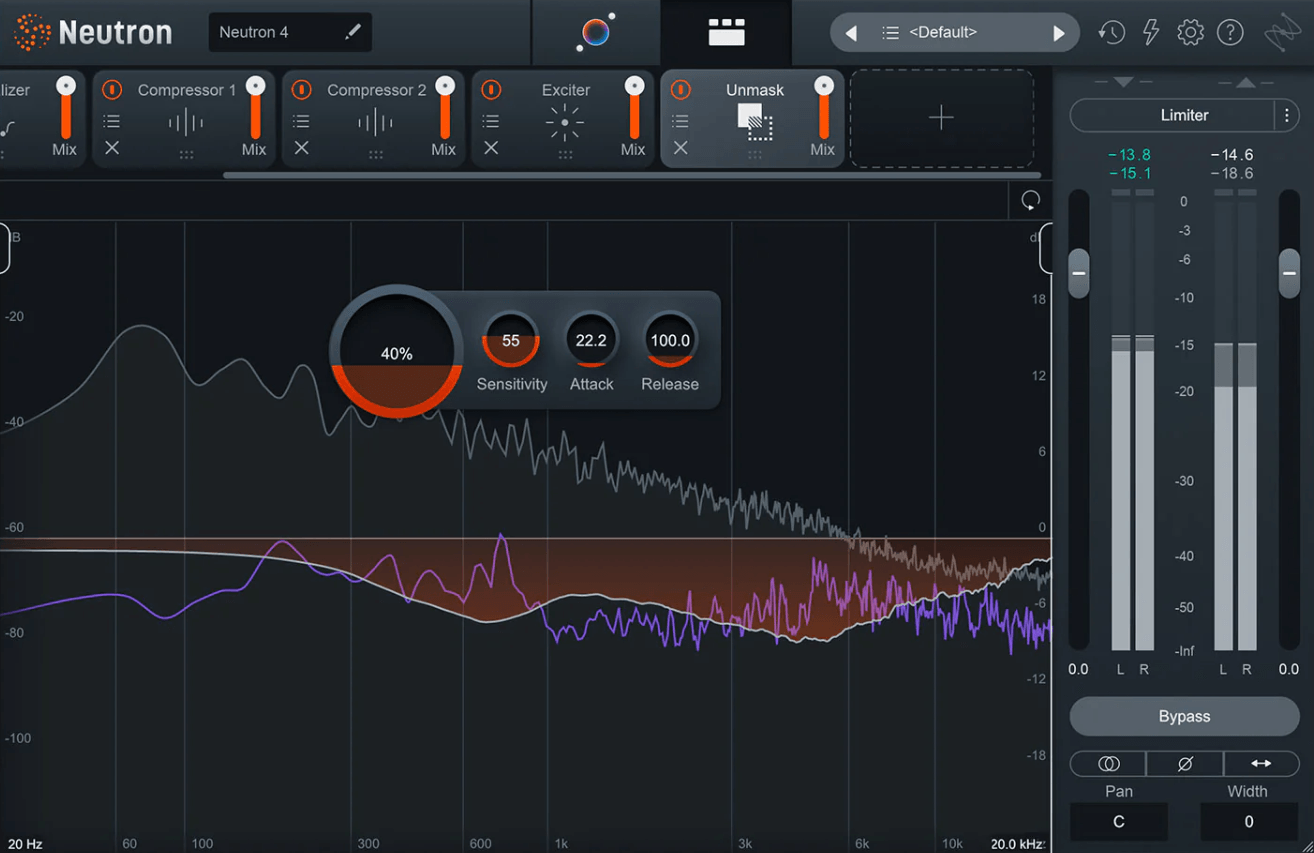
If you’ve ever been behind an audio mixer, you’ve probably seen that mysterious knob labeled “FX” and wondered, “What’s this all about?” You’re not the only one. The FX send is like the unsung hero of the audio mixing world—a feature that can make your sound go from “meh” to “wow!”
But what is it, how do you use it, and when should you use it? Buckle up, because we’re about to take a deep dive into the world of FX in audio mixers.

What is FX in Audio Mixer?
FX is shorthand for “effects,” and in the context of an audio mixer, the FX send is a specialized routing function. It allows you to send audio signals from individual channels—be it vocals, guitars, or drums—to an external effects unit. This could be a reverb unit, a delay unit, or any other effects processor.
The beauty of the FX send is that it lets you add these effects selectively. So, you could add a dash of reverb to the lead singer’s voice while keeping the bass guitar as is, giving the illusion that all instruments are playing in the same acoustic space.
One essential consideration to make FX send work exceptionally well on vocals is using a high-quality microphone. Remember, the mixer input and microphone output jacks should be similar for smooth integration. Or else, you may need to use an adapter, which may reduce the audio quality.
Therefore, if selecting a wired mic, ensure it is compatible with the audio mixer. If you’re choosing a wireless microphone, look for the mic-in/line-in specifications and make sure the receiver of the selected wireless mic model has a 3.5mm TRS connectivity output option, like the Hollyland Lark Max, so it can be easily attached to the mixer using a TRS to TRS cable.
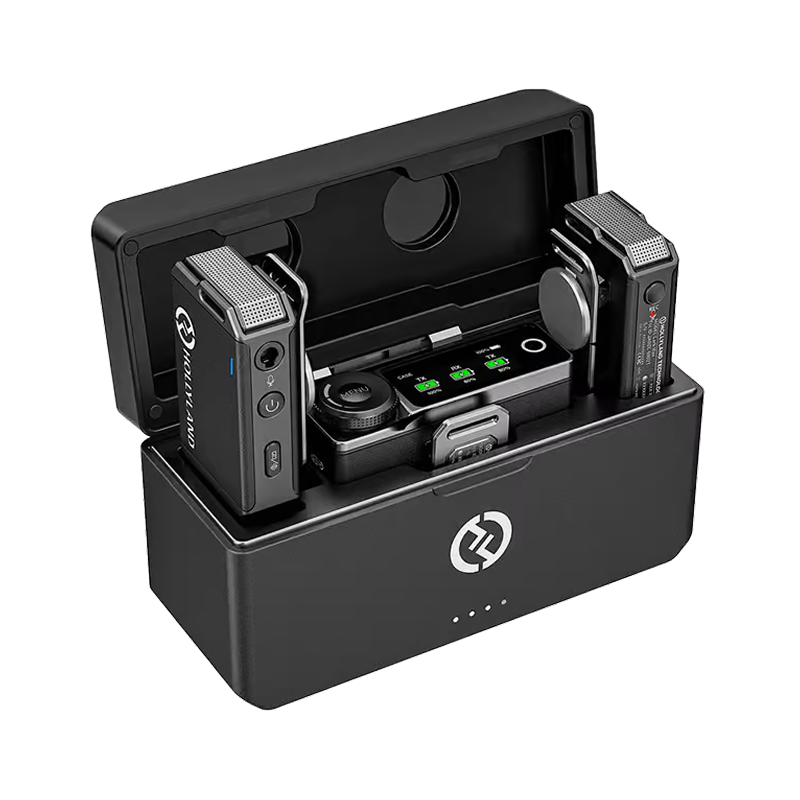


Hollyland LARK MAX - Professional Wireless Microphone
A professional wireless microphone system featuring studio-quality audio with advanced noise cancellation.
Key Features: Studio-Quality Audio | Magnetic Attachment | 8GB Internal Recording
The Technical Side of Things
The FX send is not just a “set it and forget it” feature. It requires a nuanced approach. You’ll need to adjust the levels for each channel you’re sending to the external effects unit. This is crucial because too much effect can make the sound muddy, while too little will make it unnoticeable. The key is to find that sweet spot where the effect enhances the sound without overpowering it.
How Do I Use It?
To get started, you’ll need to make sure your effects unit is connected correctly. This means patching the output of the mixer into the input of the external unit, and connecting the return jack from the external unit back to one of your mixer’s aux returns. Once this is set up, you can start experimenting with different FX sends.
Setting Up Your FX Send
Before you start turning knobs, it’s essential to set up your FX send properly. Connect the FX send output from your mixer to the input of your external effects unit. Then, connect the output of the effects unit back to an auxiliary input on your mixer. This creates a loop that allows you to add effects to the sound.
Adjusting Levels and Selecting Channels
Once everything is connected, you’ll need to select which channels you want to send to the FX unit. On most mixers, each channel will have an FX knob. Turn this knob to adjust the level of the effect for that specific channel. Start with a moderate setting and adjust as needed during sound check or even during the live performance.
When Should I Use It?
The FX send is a great tool for adding extra layers to your sound. When used effectively, it can add depth and texture to your mix while still maintaining clarity. You can also use external effects units to create entirely new sounds, such as delays, reverb, chorus, and even distortion.
Live Performances
The FX send is invaluable during live performances. It allows you to add depth and dimension to the sound, making the performance more engaging for the audience. However, the venue’s acoustics can affect how you use the FX send. Always do a sound check to adjust the FX levels according to the venue.
Studio Recordings
In a studio setting, the FX send can be used to add effects post-recording. This gives you more control over the final sound, allowing for a more polished end product. However, it’s crucial to not go overboard with effects, as it can make the recording sound artificial.
The Importance of FX Presets
FX presets are pre-configured settings that can be saved and recalled at a later time. These are incredibly useful, especially for sound engineers who work in multiple venues or handle different genres of music. Presets can save you a lot of time during setup and sound checks. Imagine having a preset for a jazz ensemble and another for a rock band; switching between the two becomes a breeze.
How to Utilize Presets Effectively
Most modern mixers with digital interfaces allow you to save and recall presets. To utilize this feature effectively, start by creating a preset during a rehearsal or a sound check. Fine-tune the settings until you’re satisfied, and then save it.
The next time you’re in a similar setting or working with the same band, you can recall the preset and only make minor adjustments as needed. This not only saves time but also ensures a consistent sound quality.
Why FX is Crucial in Digital Media

The rise of podcasting and streaming has made the role of FX in audio mixers more critical than ever. Unlike live performances where the acoustics of the venue play a significant role, digital media often lacks that natural reverb and ambiance. Here, FX can add that missing depth and make the audio more engaging. For instance, a subtle reverb can make a podcast sound less like it was recorded in a small room and more like a professional studio.
Tips for Using FX in Podcasting and Streaming
- Subtlety is Key: Unlike live performances, where the effects might need to be more pronounced, digital media usually benefits from subtler effects.
- Voice-Specific Effects: When podcasting or streaming, you’re often dealing primarily with spoken word. Tailor your effects to enhance speech clarity. A slight compression or a touch of equalization can go a long way.
- Test and Iterate: Always test your settings before going live or recording a session. Make a short test recording, listen to it on different devices like headphones, laptop speakers, and even a car stereo. This will give you a well-rounded view of how your audience will experience the audio.
Conclusion
Understanding the FX send on an audio mixer is like unlocking a secret level in a video game—it opens up a world of possibilities. Whether you’re a seasoned sound engineer or just starting out, mastering the FX send can significantly elevate your audio game.
So go ahead, experiment with different settings, and don’t be afraid to get creative. Just remember, practice makes perfect, and the more you use it, the better you’ll get at it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About FX in Audio Mixers
What does FX mean on an audio mixer?
FX stands for “effects” in the context of an audio mixer. The FX send is a specialized routing function that allows you to send audio signals from individual channels to an external effects unit. This could be a reverb, delay, or any other type of effects processor. The purpose is to add specific effects to certain instruments or vocals selectively, enhancing the overall sound quality.
How do you use FX on a mixer?
Using FX on a mixer involves a few steps:
- Setting Up: Connect the FX send output from your mixer to the input of your external effects unit. Then, connect the output of the effects unit back to an auxiliary input on your mixer.
- Channel Selection: On your mixer, each channel will typically have an FX knob. Turn this knob to send that channel’s audio to the external effects unit.
- Level Adjustment: Use the FX knob to adjust the level of the effect for each channel. Start with a moderate setting and adjust as needed.
- Sound Check: Always do a sound check to make sure the effects levels are appropriate for the venue or recording environment.
What does FX booster mean?
An FX booster is not a standard term in audio mixing, but it could refer to a device or software that amplifies or enhances the effects being applied. It could boost the signal going to the effects unit or intensify the effects themselves. Always refer to the specific product’s manual for accurate information.
What is the difference between aux and FX mixer?
Both aux (auxiliary) and FX (effects) sends in a mixer serve the purpose of routing audio signals, but they are used differently:
- Aux Send: Typically used for sending a mix of channels to stage monitors or headphones. It can also be used for external effects but is more versatile in its applications.
- FX Send: Specifically designed for sending individual channels to an external effects processor. It’s more specialized and often has fewer customization options compared to an aux send.
How loud should FX be in a mix?
The volume of the FX in a mix depends on the desired outcome and the context. In a live setting, you might want more noticeable effects to captivate the audience. In a studio recording, subtlety is often key. A good rule of thumb is to start with a moderate level and adjust based on the venue, the type of music, and the instruments involved. Always trust your ears and make adjustments during sound checks.
What is the purpose of sound FX?
Sound FX (effects) serve to enhance the auditory experience, whether it’s in a live performance, a studio recording, or even in film and video production. They can add depth, emotion, and realism to the audio. For example, reverb can make a small room sound like a large hall, and delay can add a sense of space and dimension to a guitar solo.






























.png)
.png) Français
Français .png) Deutsch
Deutsch .png) Italiano
Italiano .png) 日本語
日本語 .png) Português
Português  Español
Español