In the realm of audio recording and communication, microphones assume a pivotal role. These small yet powerful devices are the unsung heroes behind crystal-clear voiceovers, mesmerizing music performances, and seamless video conferencing. Among the various aspects of microphones, the connectors they employ are of utmost importance.
Two connectors that often take the spotlight in the audio world are TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) and TRRS (Tip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve). To anyone involved in the audio equipment scene, whether you’re a musician, a podcaster, or simply a tech enthusiast, having a firm grasp of the disparities between these connectors is paramount.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a journey to delve deep into the nuances of TRS and TRRS microphones, unravel their diverse applications, and highlight the key distinctions that set them apart. So, whether you’re looking to fine-tune your audio setup, enhance your recording capabilities, or simply satisfy your curiosity about audio technology, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
What Are TRS and TRRS Connectors?
Understanding the differences between these connectors is essential for anyone working with audio equipment, whether you’re a musician, podcaster, or tech enthusiast.
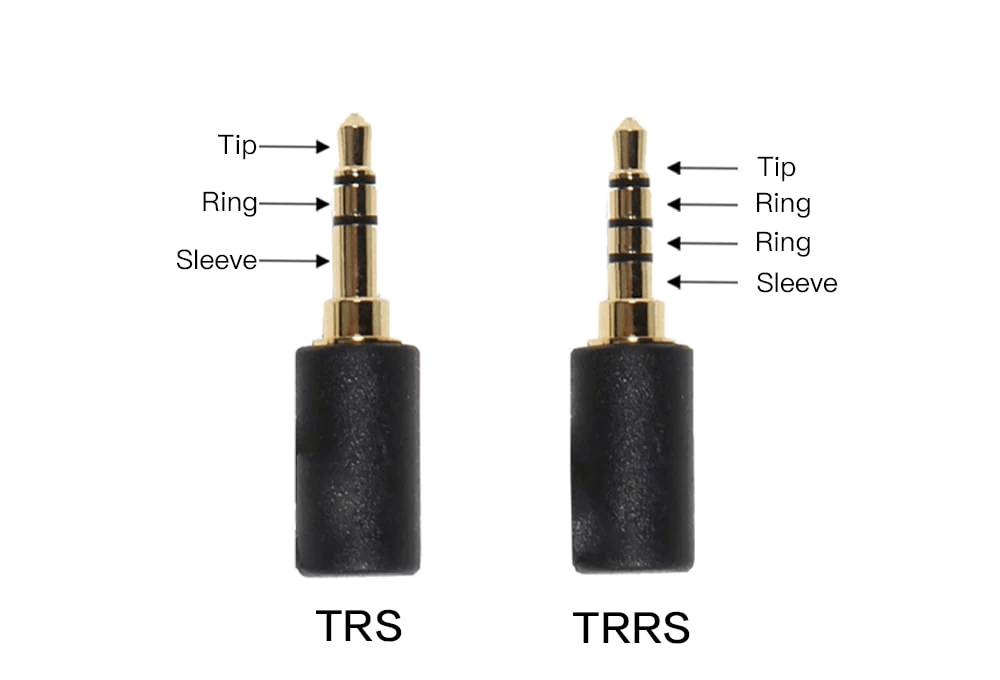

TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) Connector
The TRS connector, characterized by its three segments – Tip, Ring, and Sleeve, is a widely used audio connector. Each segment serves a specific purpose:
- Tip: The Tip is responsible for carrying the microphone’s signal. It is the primary conductor for audio transmission.
- Ring: The Ring segment is often used for additional functions such as stereo audio, balanced audio, or control signals in various applications.
- Sleeve: The Sleeve serves as the ground connection, ensuring electrical continuity and reducing interference.
TRRS (Tip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve) Connector
The TRRS connector builds upon the TRS design, adding an extra Ring segment. This additional segment enables the transmission of both audio and microphone signals, making TRRS connectors popular in mobile devices and hands-free headsets.
- Tip: The Tip still carries audio signals, just like in TRS connectors.
- Ring 1: The first Ring can carry additional audio channels or control signals.
- Ring 2: The second Ring typically carries the microphone signal.
- Sleeve: The Sleeve remains the ground connection.
Applications of TRS and TRRS Microphones Connectors
Now that we’ve covered the basics of TRS and TRRS connectors, let’s delve into their respective applications:
TRS Microphones Connector
- Professional Audio Equipment: TRS connectors are prevalent in studio-grade microphones, mixers, and audio interfaces. They are known for their balanced audio transmission, which reduces interference and noise, making them ideal for high-quality recordings.

- Musical Instruments: Many musical instruments, such as electric guitars and keyboards, use TRS connections for audio output. These connectors ensure clear and reliable sound transfer.
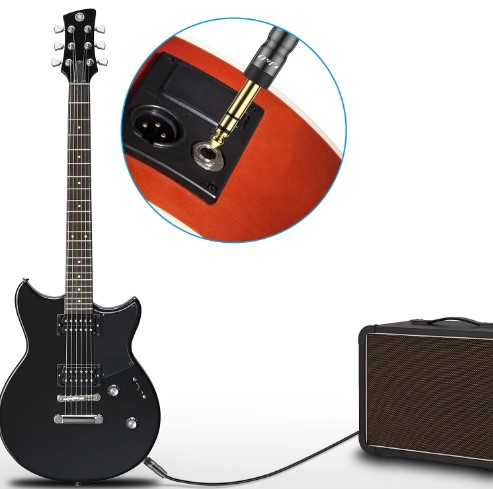

- Stage and Live Performances: TRS connectors are often used in stage and live sound setups, offering robust connections that can withstand the rigors of live performances.
TRRS Microphone Connector
- Mobile Devices: TRRS connectors are commonly found in smartphones, tablets, and laptops. They allow users to connect headphones with built-in microphones for voice calls, video conferencing, and audio recording.
- Hands-Free Headsets: Headsets designed for gaming or hands-free communication often use TRRS connectors. These headsets incorporate both audio and microphone functionality in a single plug.
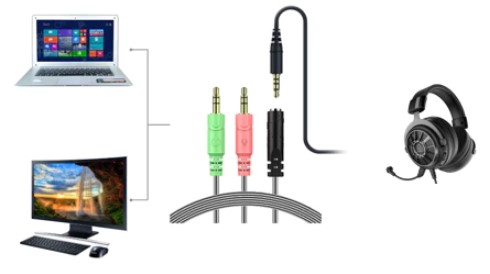
- Video Content Creation: Content creators frequently use TRRS microphones for vlogging and online streaming, as they can capture high-quality audio while remaining compatible with mobile devices.
Key Differences Between TRS and TRRS Microphones
Now that we’ve explored their applications, let’s highlight the crucial distinctions between TRS and TRRS connectors:
- Audio vs. Audio + Mic: The primary difference lies in their functionality. TRS connectors transmit audio signals only, while TRRS connectors transmit both audio and microphone signals.
- Number of Segments: TRS has three segments (Tip, Ring, Sleeve), whereas TRRS has four segments (Tip, Ring 1, Ring 2, Sleeve).
- Compatibility: TRS microphones are best suited for professional audio equipment, instruments, and stage setups, whereas TRRS microphones are tailored for mobile devices and hands-free communication.
- Balanced vs. Unbalanced: TRS connectors are often associated with balanced audio, which reduces interference. TRRS connectors are typically unbalanced.
TRS Connectors and Their Variations
TRS connectors, short for Tip, Ring, Sleeve connectors, are commonly employed in stereo audio setups. The additional ring in these connectors allows for the segregation of left and right audio channels, making them ideal for stereo applications. They can also be used for balanced audio configurations, with the audio signal transmitted through the tip while the ground connection is established via the sleeve. These connectors typically come in the ¼-inch variety, and they consist of three distinct sections, each serving a specific purpose. The sleeve functions as the ground, the tip as the positive leg, and the ring as the negative leg.
¼” Balanced Line TRS Connector
The ¼-inch TRS cables are frequently utilized for balanced audio signals, making them suitable for longer cable runs exceeding 25 feet. These cables incorporate a shielding layer and two signal wires (or a ground and two legs). An example of a high-quality ¼” TRS balanced line cable is the RapcoHorizon¼” TRS balanced line cable. This male-to-male TRS stereo cable facilitates the connection of devices to auxiliary inputs seamlessly.

3.5 Millimeter TRS Connector
3.5 mm TRS cables are primarily employed for stereo signals. They have the capability to carry both left and right signals because TRS cables include dedicated left and right polarized legs, along with a ground connection for balanced signal transmission. Specifically, the ring and tip segments are responsible for carrying the left and right signals, while the sleeve connects to a third conductor, establishing a common path that completes the circuit for both the right and left wires.

Unbalanced vs. Balanced Signals
While a TRS cable can effectively transmit balanced mono signals, it transitions into an unbalanced configuration when dealing with stereo signals. In this context, instead of employing the Common Mode Rejection technique to eliminate noise when the same signal travels through both the left and right legs of the cable, the TRS cable is used to transmit the two stereo signals independently for the left and right ear pieces or cups of your audio listening device.
TRRS Connectors and Their Variations
TRRS connectors, or Tip, Ring, Ring, and Sleeve connectors, are commonly found in TRRS cables. The name itself reflects the presence of two additional “R” segments, setting them apart from TRS connectors and earning them the moniker TRRS. These connectors are designed to accommodate not only the left and right audio channels but also the microphone channel, making them versatile for various audio applications. TRRS connectors consist of four sections, allowing devices to establish four connections or channels.
¼-Inch and 3.5-Millimeter TRRS Connector
While ¼” TRRS cables exist, they are relatively rare and might not be easily accessible. In contrast, the 3.5mm TRRS cable is a common and readily available item. These cables are typically used with headphones that have an integrated microphone. The extra “R” in the TRRS cable is responsible for carrying the microphone signal, distinguishing it from standard TRS headphones and microphones. If your device features a ¼” port, it’s more likely to be a TRS port rather than a TRRS one.

Advantages of TRRS and the Common Pathway
Essentially, a TRRS connector is an enhanced version of the TRS connector, incorporating an additional “R” to enable four-channel connections. This is especially useful for stereo headphones with a microphone attached to a single cable, as it accommodates left and right audio channels along with the microphone. The fourth channel functions as the common pathway, ensuring complete circuitry. To extend the reach of TRRS headphones, you can utilize a 3.5mm TRRS headphone extension cable equipped with a microphone.
TRS and TRRS Interoperability
TRRS connectors can sometimes be interoperable with TRS connectors when employed for additional microphone input, enhancing stereo output capabilities. However, this compatibility depends on how the contacts are utilized. There are instances where they are not compatible, such as when connecting TRS microphones to the TRRS socket of a smartphone. In such cases, the use of an adapter like the Rode SC4 or a similar TRS-to-TRRS adapter is required to facilitate the connection.

Similarly, an adapter also plays a vital role in several wireless microphone systems, such as the Hollyland Lark M2. The Lark M2 gives you the option to utilize a 3.5mm TRS to a 3.5mm TRRS cable to widen its compatibility.
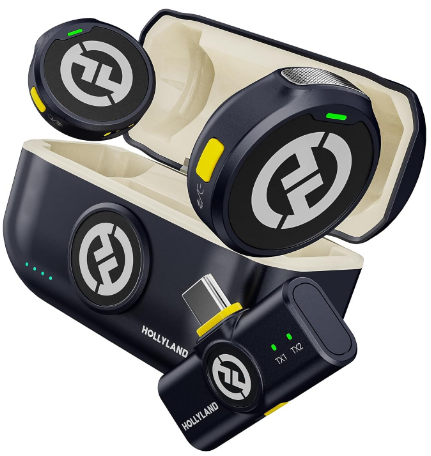


Hollyland LARK M2 - Mini Lavalier Microphone
An incredibly lightweight and compact wireless button microphone that captures high-fidelity audio.
Key Features: 9g Button Size | 48 kHz/24-bit | 40 Hours Battery
However, depending on the brand, some microphones may include the TRS to TRRS adapter within the package while others don’t, requiring you to buy it separately. Although using an adapter cable should not be supposed to degrade the mic’s actual performance, it is wise to use an adapter from a reliable company to ensure high audio quality.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of audio technology, the choice between TRS and TRRS connectors is a decision that can significantly impact your audio experience. As we wrap up this comprehensive guide, let’s recap the key takeaways:
TRS Connectors: Ideal for professional audio setups, instruments, and stage performances, TRS connectors excel in delivering balanced audio signals and reducing interference. They are the go-to choice for anyone seeking top-notch audio quality in their recordings.
TRRS Connectors: Tailored for mobile devices and hands-free communication, TRRS connectors are the bridge between audio and convenience. They effortlessly handle stereo audio and microphone signals, making them indispensable for smartphone users and content creators on the go.
Understanding the nuances of these connectors empowers you to make informed decisions when selecting audio equipment, whether it’s for creating music, recording podcasts, or simply enjoying your favorite tunes.
We value your thoughts and opinions. If you found this guide helpful or have any questions, suggestions, or personal experiences related to TRS and TRRS connectors that you’d like to share, please feel free to leave your feedback below. Your insights can help us continue to provide valuable content and assist others in their audio journey. Thank you for being part of our community, and we look forward to hearing from you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use TRS instead of TRRS?
Yes, you can connect a TRS stereo headphone (without a microphone) to a smartphone or tablet with a TRRS socket. The TRS aligns with the correct connectors in the outer portion of the socket.
Can TRS be used for a microphone?
While a TRS (Tip Ring Sleeve) plug has three conductors and is available in 1/4″ and 3.5mm sizes, it’s commonly used for stereo unbalanced audio. It can be used for mono balanced connections as well, including microphone-level, line-level, or speaker-level applications.
Will a TRRS mic work in a TRS jack?
When you plug a TRS headset into a device, the microphone will stay active, but the internal speakers will turn off. Similarly, a TRRS headset can be used with a TRS port, but the microphone channel may not be active.
Is 3.5mm the same as TRRS?
No, they are not the same. 3.5mm and TRRS refer to different aspects of connectors. 3.5mm denotes the size of the connector, while TRRS indicates the sections on the connector (Tip, Ring, Ring, Sleeve).
What cable should I use for a microphone?
XLR connectors with 3 pins are typically used for microphones or balanced line-level signals in audio. They are commonly seen connecting microphones to mixers and linking various outputs to powered speakers.
Where do I plug my mic in?
If your microphone has an 1/8 inch (3.5mm) jack, plug it into the corresponding port on your device. If it has a USB jack, connect it to an available USB port on your computer.
Does the cable affect mic quality?
Cable quality can impact how well cables reject electromagnetic or radio frequency interference. In a clean environment without interference, there should be no noticeable difference. However, in situations with high interference, cable quality may make a difference.
Is TRRS a stereo connector?
TRRS connectors are highly versatile and can be used for mono, stereo, and microphone signals. They have four segments (Tip, Ring, Ring, Sleeve), accommodating various audio configurations.
Is a microphone jack the same as an aux jack?
No, microphone jacks and headphone jacks are not the same, even if they use similar connectors like TRS or XLR. Microphone jacks are designed to receive microphone signals, while headphone jacks are meant for sending audio signals to headphones.
What is better, a USB or audio jack microphone?
USB microphones are affordable and straightforward, with built-in signal processing hardware. 3.5mm (audio jack) microphones can be more expensive but might offer better audio quality. The choice depends on your specific needs and budget.






























.png)