Among various microphone types, one with ribbons is highly recommended. While these mics can capture sounds in great detail, they also have a bit of a unique appearance compared to other microphones. But did you know that ribbon microphones are further divided into categories? And why are these mics expensive compared to other devices?
So, if you want to know all the basic information about ribbon microphones, this is the perfect page to read. You will learn the pros and cons of this mic. Plus, you will uncover the ideal scenarios for using it.
What is a Ribbon Microphone?

If you have knowledge of how a dynamic microphone works, you can quickly grasp the concept of a ribbon mic. However, instead of a coil that moves in the magnetic field of a dynamic mic, ribbon microphones have a thin metal plate or strip along with the component that modifies sound into electrical signals.
A ribbon microphone usually welcomes sound from the back and front areas. It doesn’t capture sound from the left and right sides in high quality and adequately. This gives a massive hint about its polar pattern, which is “Figure 8” or bi-directional.
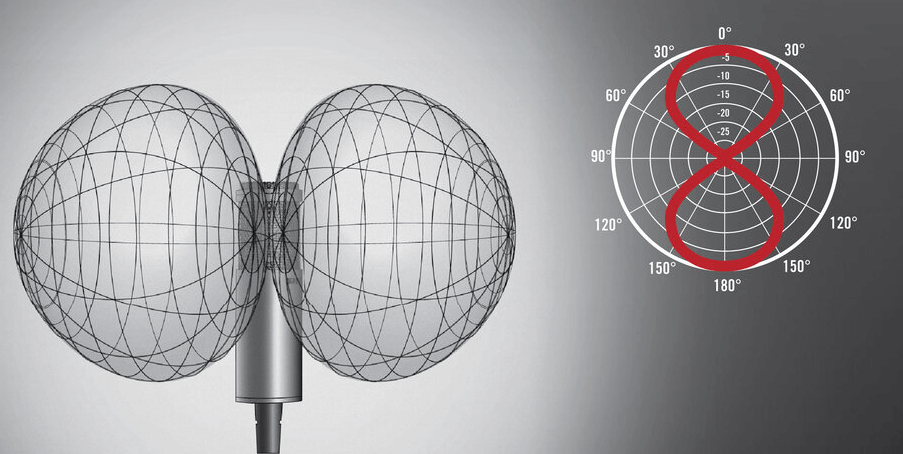

To make this more understandable, assume your ear is a ribbon microphone. It can listen to the sound sources from the front and behind, just like if two people are talking, one at the front and another behind your back, and you’re standing in the middle. Your ears will be able to listen to both of them. However, you may need to turn your head to the left or right to better listen to the sound from the sides.
So, if you desire to record vocals or instruments in the front and back positions of the microphone, a ribbon microphone is a great solution. It is also observed that sounds captured through these microphones have a unique tone.
Passive vs. Active Ribbon Microphones
Technically, you can box ribbon microphones based on two types.
The passive ribbon mics don’t possess fancy components inside them to sound good. The right kind of preamp is enough to ensure high sound quality. Keep in mind that passive ribbon microphones require high-impedance preamplifiers, as they cannot perform at low volumes. If the preamp has an extremely low impedance, it changes the quality, and the mic loses its ability to pick up bassy parts and high-pitched notes well.

Golden Age Project R1 MKII Passive Ribbon Microphone
But, many professionals know how to take advantage of this issue. They consider this situation as if having a stereo with a bass knob. Whenever you find the bass sound overlapping treble, you can use the knob to adjust its intensity.
Unlike passive microphones, active ribbon microphones require phantom power, allowing them to be used at any impedance level. Because active ribbons are newer inventions, they have electrical components inside them that make them work with any preamplifier. Moreover, active ribbon microphones are reliable with preamps and offer a bigger sound output compared to passive mics.

sE Electronics RNR1 Rupert Neive Signature Active Ribbon Microphone
So, in a nutshell, passive ribbon mics sound impeccable when used with the right preamps. On the other hand, active ribbon microphones don’t require special preamps to sound great.
When did Ribbon Microphones Emerge?

This section highlights the history of ribbon microphones, and guess what? It is not boring at all!
Two German scientists and inventors, Erwin Gerlach and Walter Schottky, with a specialization in physics, combined their intelligence to produce the first ribbon microphone in the early 1920s.
They are still one of the pioneers in bringing technology that changed the dynamics of the sound recording and broadcasting worlds. Due to their quality of capturing warm sound, these microphones quickly made their way into the hearts of sound engineers, singers, producers, and voice actors. However, by the 1920s, ribbon microphones were still not commercialized.
Then came the 1930s, when people saw the first available ribbon microphone go into the market and take it by storm. The RCA, a robust mic in the industry, changed everything with its strong pipeline and expansive branding, which let the mic brand dominate the industry. Very soon, other microphone manufacturing companies also began to offer their ribbon mics, which was necessary to maintain the balance in the industry.

If you peek into ribbon mic technology, you won’t find any secret ingredient. The entire mic is based on the fundamental principles of physics. However, its solid, unique, attractive construction makes it distinctive from other microphone types.
How do Ribbon Microphones Work?
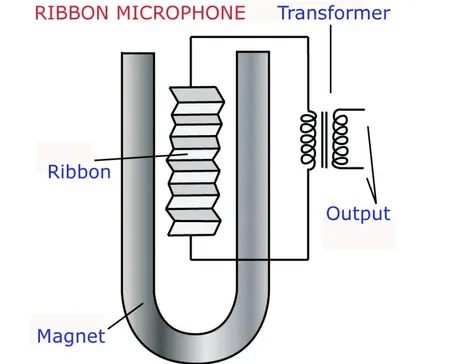
First of all, you should know that ribbon microphones are somehow relevant to dynamic mics despite not being one of them at all. They appear delicate but are quite durable. They consist of a thin, wavy metal strip or film made of aluminum alloy placed between two magnets. This piece of metal is referred to as a ‘ribbon.’
Being surrounded by the magnetic field from a permanently placed magnet, the ribbon acts in response to the received sound waves (air pressure), which vibrate the ribbon. This action intersects the magnetic lines, creating voltage or electrical signals inside the conductor.
The voltage in traditional ribbon microphones is weak. That is why a transformer (preamp) is added to the system to boost impedance and signal strength. Overall, they possess delicate components, making them outstanding at picking up sounds quickly. They can handle different audio frequencies and have a wide dynamic range.
Sound and Characteristics of a Ribbon Microphone
Ribbon microphones are popular for reproducing mesmerizing sound quality. However, they do look extremely fragile. This perception has existed for several decades due to the thin ribbons between the magnets.
Let’s take examples of some of the most common ribbon microphone models, like the Coles 4038. This brand includes a ribbon that is only 0.6 microns thick. Similarly, the AEA ribbon microphone has a ribbon measuring just 1.8 microns. And if you want to get a little extra thickness, Royer has some great options ranging from 2.5 microns to 4 microns ribbon thickness.
Now imagine that human hair is 50 times thicker than most ribbons in the microphone. Moreover, you should be very careful when handling ribbon mics. They demand a gentle touch, and you should also protect them from strong plosives or sudden passage of wind.
From a quality perspective, ribbon mics deliver magnificent sound. They capture uncolored, pure sound with natural warmth and feel. They accurately regenerate the sound of vocals and instruments, combining with the effect of the acoustics in the recording studio. But it all depends on your preference. If you want flat responses and details in your recordings, ribbon microphones may not be suitable. They are best at delivering rich low-end tones while slightly compromising high-end details to create a more realistic sound.
What are the Key Applications of a Ribbon Microphone
Ribbon microphones can be used for a wide range of applications and several sound sources, so it’s no wonder they are indispensable recording tools for professionals. Let’s uncover the main uses of ribbon mics.
1. Singing and Voiceovers
In professional environments, recording vocals with ribbon microphones is considered a luxurious practice, which is highly appreciable. These microphones can effortlessly record low-end frequencies and have incredible sensitivity, making them one of their own kind mics, as other microphone types don’t acquire such capabilities and may not replicate the warmth and depth offered by ribbons.
Additionally, many singers, voiceover artists, and audio engineers favor ribbon microphones for making vocals prominent without altering their originality. This device’s Figure 8 polar pattern makes it suitable for podcasters, as it allows both guest and host to speak in one single microphone.
2. Guitars
Despite being one of the sensitive microphones, ribbon mics easily handle too loud sound sources, including bass, electric, and acoustic guitars. Since these mics have warm and dark sounds, these characteristics complement electric guitar recordings, especially at peak volumes.
Besides, ribbon microphones’ dynamic design permits rapid transients, making them excellent for capturing electric guitar’s mid-range notes. These mics also restore the details of low-frequency tones in acoustic guitars when played on high-pitched notes, making them ideal for guitarists from various genres.
3. Drums
Ribbon microphones can flawlessly capture overhead drum sounds with weight and depth. These mics are great at preserving the details and clarity of drum recordings. Moreover, they also add impressive room ambience by eliminating high-end frequencies. Besides, their Figure 8 polar pattern allows stereo recordings. As a result, it effortlessly blends the entire drum kit sound with room sound.
4. Strings Instruments
Ribbon microphones can capture all major string instruments just the way they sound in movies. Again, a big thanks to its polar pattern that records minute sound details with room ambience.
5. Wind Instruments
Instruments like woodwind and brass can be recorded without including harsh tones, which naturally occur due to high pitches. Ribbon microphones can also reduce the “honk of horns” effect as they can handle high sound pressure levels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ribbon Microphones
Every invention has a good and a not-so-good side. The same goes for ribbon microphones. So, let’s uncover their benefits and flaws.
Pros of Ribbon Microphones
- Great for capturing high-frequency notes without harshness
- Figure 8 ensures the mic provides stere and spatial recording possibilities
- The mic even records delicate sounds for enhanced dynamics in recordings
- A ribbon mic captures audio with outstanding accuracy, especially for vocals and acoustic instruments
- It adds both warmth and depth to your recordings, making them more considerable for genres, including blues, jazz, pop-rock, western classical, and more
Cons of Ribbon Microphones
- Occasional maintenance required
- More expensive microphone than other types
- It has a fragile structure compared to condenser and dynamic mics
Ways to Maintain and Care for Ribbon Microphones
Ribbon microphones should be treated with a soft touch to ensure optimal performance for years. Here are a few tips for taking good care of the mic.
a. Save them From Air Blasts
It is necessary that you prevent a ribbon microphone from compelling air blasts as they can severely damage delicate components. Ensure the airflow never comes in direct contact with the microphone’s head, especially when cleaning the surface. Moreover, whenever you try to record in an open environment, make sure it is not a windy day. Why all these precautions? Because the ribbon inside the microphone is extremely sensitive to air pressure. Rough airflow can damage the entire inside mechanism.
b. Keep It Safely
Keep the ribbon mic in a safe and dry location when it is not in use. Do not store it in areas where accidental bumps or knocks have high chances. And make sure the case, box, or whatever object you have to store the mic is moist-resistant.
c. Routine Maintainenace
Some ribbon microphones may require frequent servicing, while others can be maintained occasionally. The maintenance involves in-depth inspection of the body and components to ensure they perform well. It is also a good idea to replace ribbons after a few months or years so you can keep on experiencing high performance. However, never change the ribbons on your own if you’re not a certified technician.
Choosing the Right Ribbon Microphone
Ribbon microphones are expensive, so you can’t risk buying a mic that doesn’t meet your needs. If you want to buy a ribbon microphone, make sure you consider the following factors.
a. Application
Ribbon microphones can be a great option if you want to capture high-frequency sounds in exceptional detail. These mics can pick up nuances in audio, whether recording vocals or instruments. They isolate sound well enough to make it clear and deep.
b. Frequency Response and Sensitivity
Frequency response and sensitivity are two vital factors to look into when selecting a ribbon mic. These mics are best if you want to record vocals without exaggerating specific audio frequencies since they offer a balanced frequency response. However, strive for values that range from 15Hz to 20kHz.
Likewise, sensitivity decides how loud or soft notes a mic can pick and reproduce. It is suggested that a device with a nominal sensitivity be chosen because higher sensitivity can also add too much environmental noise.
c. Durability and Build Quality
A robust ribbon microphone can resist rough handling on a daily basis. Therefore, choose a mic made with strong materials so that it has minimal chances of getting damaged even if you frequently travel with it. This feature will also increase the microphone’s life, even for decades.
d. Budget and Features
Your budget decides the number of options you have. It helps you find a ribbon mic that fulfills your needs without breaking the bank. So, if you have a low budget but still need a ribbon microphone for your home studio, look for a device with basic features. If you search for advanced functions, those mics will cost a lot.
Conclusion
Ribbon microphones are not new inventions but have entertained audiences for almost 100 years. They are expensive microphones due to the metallic ribbon inside the structure, which ensures high-quality audio recording of vocals. Moreover, these microphones can record all strings and wind instruments and are easy to maintain. However, they are very sensitive to a sudden gust of air and should be kept away from wet places.
If you’re exploring microphone choices for different recording contexts, you might also consider the versatility of a wireless lavalier microphone. Offering convenience and freedom of movement, lavalier mics are ideal for interviews, presentations, and video productions where discreet, hands-free audio recording is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Ribbon Microphone
Q1. Can ribbon microphones be used for live performances?
Yes, ribbon microphones can be used for live concerts and events. In fact, these mics were the first choice for live performances from the 1930s to the 1970s.
Q2. How are ribbon microphones different from condenser microphones?
The basic difference is sensitivity. Ribbon microphones usually have a sensitivity compared to condenser mics. Also, these mics have a Figure 8 polar pattern, something that is not a typical feature of condenser mics.
Q3. Are ribbon microphones suitable for recording all types of instruments?
Ribbon microphones are suitable for brass, wind, and string instruments. They can also be used to record drums and guitars.
Q4. How do I prevent damage to my ribbon microphone?
Never blow into any ribbon microphone for any purpose. Keep it away from lying around on the surface. Take extraordinary measures to safeguard the mic from air blasts (use windscreen or foam when using outdoors).
Also, before adding phantom power to the system, ensure the microphone supports the voltage given by phantom power. Otherwise, the ribbon foil inside the microphone will be destroyed. Besides, be gentle when touching or carrying the microphone and keep it away from dust and wetness.
Q5. Can I use phantom power with a ribbon microphone?
Yes, you can use it only if it supports phantom power.
Q6. What makes ribbon microphones more expensive than other types?
The ribbon or foil is the most expensive component of a ribbon microphone, making it more costly than other mics.
Q7. How do I choose the right preamp for a ribbon microphone?
Choose a preamp with a high clean gain. It will help you record soft sounds correctly.
Q8. Can ribbon microphones be repaired if damaged?
It depends on the intensity of the damage. An expert technician can replace the ribbon foil. However, if the entire mechanism has been electrified (due to irregular voltage or wrong phantom power), it may be completely destroyed.
Q9. Can ribbon microphones have a Figure 8 polar pattern?
Most ribbon microphones have a “Figure 8” polar pattern. It won’t be incorrect if you say it’s a standard pattern in ribbon microphones.
Q10. What are iconic ribbon microphone models, and what are their uses?
The Coles 4038 is one of the most iconic microphones made by the BBC in the mid-1950s. It has been used mainly for vocals by iconic and legendary bands like Led Zeppelin and The Beatles. Similarly, the RCA 44 Ribbon has been used as a vocal microphone by Josh Homme, Sinatra, Nat King Cole, and the superstar of the century, Elvis Presley.






























.png)