Sample rate is very important in determining the fidelity and quality of sound. Sample rates allow you to capture detailed audio with a true representation of the original sound. Moreover, it permits your audio systems to regenerate a wide range of frequencies accurately.
Unfortunately, many potential and new music producers, engineers, and musicians don’t go into the technical depth of sample rates. Instead, they focus on the glitters of DAWs and the mesmerizing tones of virtual instruments for audio recording, not realizing that the good quality of sound also depends on several other factors, including sample rates.
So, today, you will learn about what is sample rate in audio. Why understanding the Nyquist theorem is essential and how it is related to sample rate. Moreover, you will explore sample rates’ impact on audio quality, common sample rates, and their relation with bit depth.
What is Sample Rate in Audio?
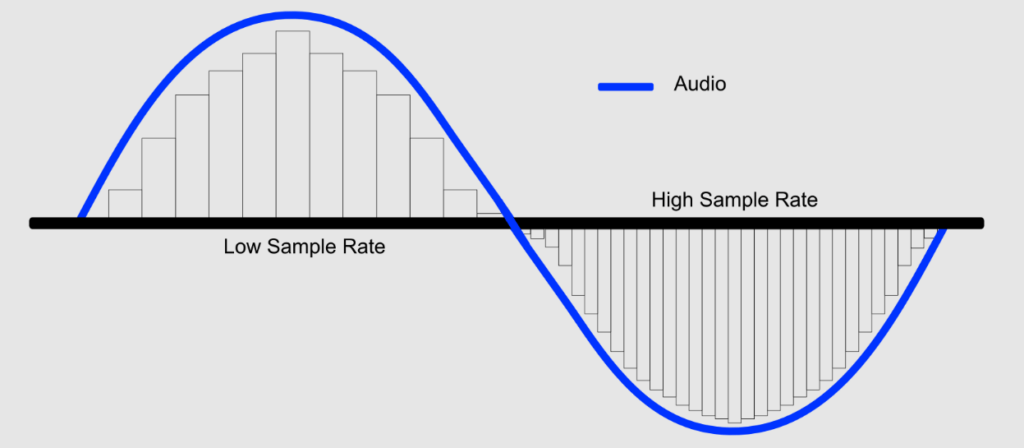
Sampling frequency, also called sample rate, is one of the main scales in the digital audio world. It means the number of audio samples in waveform per second. These samples hold audio signals’ volume at regular intervals. And when these signals are played back, they rebuild the continuous waveform pattern of the audio. Therefore, the sample rate helps you figure out how clean the audio signal is exhibited in the digital format.
The sample rate is generally calculated in Hertz (Hz), which demonstrates cycles in one second. The most common and widely used sample rate in audio is 44kHz, followed by 48kHz and 96kHz. However, there are also higher rates which are used in different scenarios. To understand this in a better way, imagine a CD in audio format that utilized a 44.1kHz sample rate. It means that there are 44,100 samples present in the audio signal in each second.
Understanding Sample Rate in Audio through Nyquist Theorem
Before you proceed further, it is important that you have your concepts clear about the sample rate in audio, and the Nyquist Theorem is the best way to do that. Harry Nyquist, a Swedish-American communication and electrical engineer, proposed this theorem that offers a basic principle for digital audio sampling. According to this theorem, to represent any analog signal in a digital format, the sample must be of the highest frequency (twice as high, at least).
For example, assuming that humans hearing range is between 20Hz to 20kHz. So, in order to correctly capture all hearable frequencies, the minimal sample rate you will need is around 40khHz. That is why an ordinary CD has a minimum sample rate of 44.1kHz since humans can hear sound at this sample rate.
But, if the sample rate does not meet the standards of this theorem (suppose it’s too low), it can cause aliasing. Aliasing is a condition that takes place when higher frequency elements of an analog signal reverse back into the digital domain, resulting in distortion and unwanted noises. Therefore, it is necessary to comply with the Nyquist theorem to ensure the correct representation of digital audio.
How Sample Rate in Audio Works?
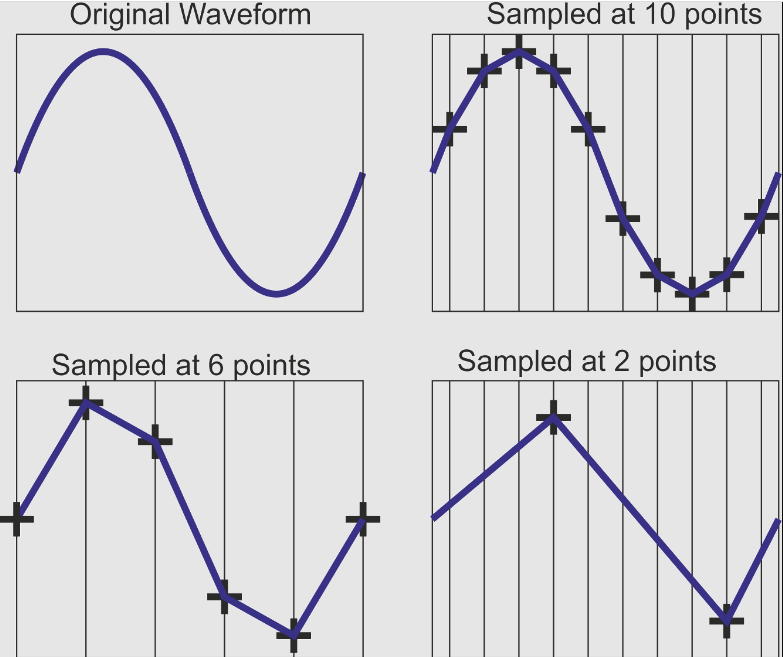
To understand the working of sample rate in audio, you first need to understand the entire process of transforming an analog signal into a digital audio signal. Analog waveforms are continuous, which means they are comprised of infinite points. Contrarily, digital audio is discontinuous and contains individual samples close to the sound’s original signal. So, the sample rate discovers how routinely the samples are extracted.
Imagine you are watching your favorite show, and there is a part where still images appear in the series. So, consider those still images as your sample rate, which means the number of frames in a second you find in the show. A high frame rate will allow smooth motion with more realism. In contrast, a low frame rate will turn motion into a choppy experience. The sample rate in audio works in the same way. Higher sample rates will lead to the correct portrayal of an audio signal. Conversely, a low sample rate will result in a loss of audio fidelity and detail.
Human Depiction of Sample Rate in Audio

The human ear is usually a reference point when talking about audio quality and sample rates. Humans normally hear sound at sample rates ranging from 20Hz to 20,000Hz. This range makes several people wonder why high sample rates are important in audio recording. The Nyquist theorem discussed earlier in this article gives the right answer. Although human hearing is limited to 20kHz, the transients and harmonics in audio usually touch higher frequency ranges. So, in order to capture these details, it is essential to use high sample rates.
Impact of Sample Rate on Audio Quality and Equipment
Sample rate influences audio quality directly. Plus, choosing the right sample rate can impact the fidelity of audio playback and recording. So, below are some factors showing how sample rate impacts different technical aspects of audio and overall music production equipment.
a. Audio Details
Sample rates impact sound details and transient response. If you’re not sure what transient is, it means the sudden change in the sound of instruments once they are being played, such as hitting the drums. Therefore, a higher sample rate allows you to capture these transients accurately.
b. Signal Fidelity
Higher sample rates represent more accurate analog signals. Why so? Because of increased sample rates, the digital audio waveform becomes similar to the original analog signal. This ensures lesser distortion and greater fidelity. This confirms that sample rates play a vital role in signal fidelity, enabling music producers to record and process high-quality analog to digital audio signal conversion.
c. Resampling
It is no surprise that when you try to convert different sample rates, it automatically diminishes the sound quality. In this scenario, your recording software plays a key role in copying the right sample rate compared to the original. However, it won’t work and offer precise, correct audio signals if the sound that is being converted has a lower sample rate.
That is why experts suggest recording audio at the highest sample rate to mitigate resampling needs. This helps at the time of mixing and mastering your audio without compromising the original audio quality.
d. Frequency Response
Remember, if there is a high sample rate, it will offer an extensive frequency response. This will allow you to produce and record high-frequency sound, ensuring better audio quality. This is a great advantage for professional audio recording setups, as engineers can capture suitable harmonics and nuances required to improve the quality.
For instance, when recording string instruments or cymbals in a studio at high sample rates, the recorded audio is more clean and crisp. Contrarily, capturing these sounds at a lower sample rate will lead to bad audio quality.
e. Compatibility
Before aiming for a prominent sample rate, ensure your entire audio production setup is compatible with your selected sample rate. This is because some audio devices (hardware and software) cannot support high-level sample rates. In that case, you must ensure that all your recording equipment, including DAWs, audio interfaces, and microphones, supports your desired sample rate.
f. Storage Space
Although sample rates are crucial in the world of audio, they may compel you to upgrade your system data storage capabilities to savor the benefits. What happens is that when you strive to get higher sample rates, they produce heavy data, especially when you work on big audio files, such as long-duration audio or multi-track recordings. If your existing system has less data storage capacity, saving files at a heavy sample rate will be impossible and will impact your workflow.
For instance, RODE NT1 microphones only support 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 88.2kHz, and 96kHz sample rates. So, in order to use this microphone, your recording software must align with this sample rate. Otherwise, you won’t be able to record vocals.
Classification of Sample Rate in Audio and their Applications
Depending on your requirements, different sample rates are used in various audio applications. Some of the most common sample rates in audio are:
a. 44.1kHz
44.1kHz is considered as a typical sample rate for CDs. It is widely used for music production work, especially when it comes to commercial launches. However, many people think that the time of CDs or DVDs is gone and artists release their albums on online platforms, but this is not entirely true. Most musicians still use CDs to compile their music albums for selling purposes, and Amazon is full of newly released albums by various musicians and singers.
b. 48kHz
The 48kHz sample rate is used for recording audio for films, video games, and television. Moreover, it is also a benchmark for DAWs. This sample rate offers a great balance between audio and video quality.
c. 88.2kHz / 96kHz
Both 88.2kHz and 96kHz sample rates are used for high-resolution audio. They are better than all the previously mentioned sample rates and offer enhanced audio quality for capturing ultra-fine details in music.
d. 192kHz
This is the highest sample rate in audio used in the industry where top-notch audio fidelity is needed. That is why 192kHz is highly utilized in home theaters and high-quality home entertainment systems to enhance the listener’s experience.
Relation between Bit Depth and Sample Rate in Audio
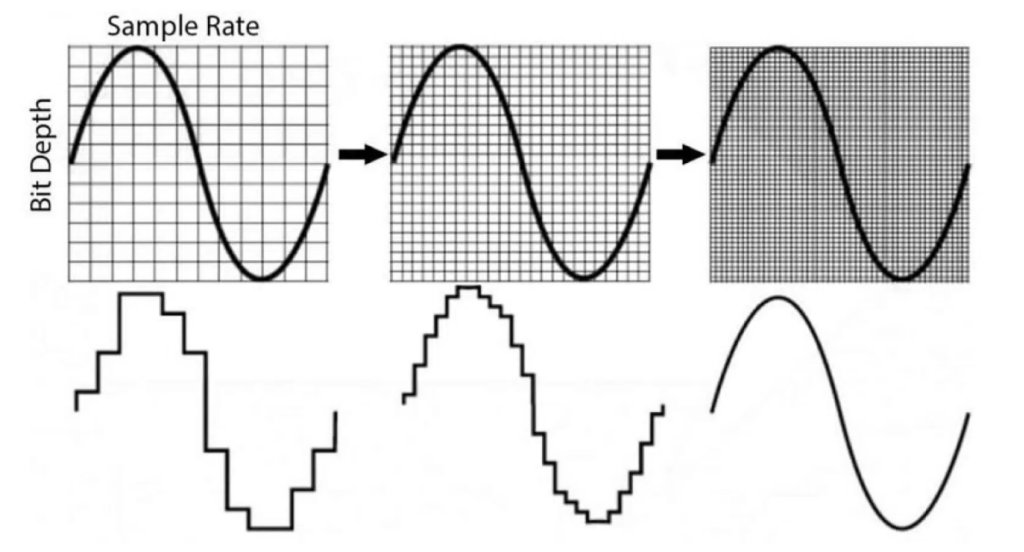
Bit depth and sample rates are often seen together at different levels. Bit depth evaluates each sample’s resolution. It describes the number of bits utilized to demonstrate the sample rate’s amplitude. Bit depths are commonly found in 16-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit values and are widely used in audio production along with sample rates.
So, it is essential to understand the relation between bit depth and sample rate, as these two elements work together to capture high-quality audio and preserve it. If a bit depth is high, it permits the fine-tuning of amplitude levels in each of the sample rates. This elevates the dynamic range and mitigates quantization noise. Therefore, higher bit depths are extremely valuable when it comes to recording soft, detailed sounds at higher sample rates to ensure uncompromised sound quality.
The Need for Conversion of Sample Rate in Audio
The process of amending a sample rate into another is called sample rate conversion. Sometimes, you may need to convert the sample rate of a specific audio file into another. This usually happens when you work with a variety of projects and you find the need to export audio and integrate it with other files or platforms.
One of the simplest examples of audio sample rate conversion is mixing a track for a film project. Suppose the video requires 48kHz audio, but you recorded the sound at 44.1kHz; therefore, you must convert the sample rate to match the project’s requirements.
You can find rich tools for sample rate conversion. However, the quality of conversion depends on the methods you follow. So, when doing this task, it is important to pick a high-quality platform that doesn’t distort your audio. Besides, you should avoid frequent sample rate conversion of the same audio file to ensure the song, music piece, or background score remains preserved in the highest quality.
Conclusion
Sample rate in audio means determining the number of audio samples in the waveform. Several engineers and experts have tried to explain the sample rate concept, but the most compelling version is the Nyquist Theorem. Although human ears can only survive 20kHz audio signals at most, the need for higher sample rates allows music producers to capture minute sound details needed for producing high-quality audio production.
Moreover, sample rates are classified into different categories, ranging from 44.1kHz to 96kHz. Besides, sample rates greatly impact several software and hardware elements of audio, such as frequency response, signal fidelity, and more. So, when striving for higher sample rates, ensure you have the right compatible tools to do the job successfully.
When aiming for clear and detailed audio recordings, selecting a microphone with the right technical specs is essential. For instance, using a high-quality wireless lavalier microphone ensures precise audio capture, helping to fully utilize your chosen sample rate and achieve the desired sound clarity.
FAQs
Q1. What is a good sample rate for audio?
Normally, 44.1kHz is the best sample rate. However, when producing music for albums or video projects, professionals also use 48kHz.
Q2. Which is better, 48kHz or 44.1kHz?
Experts recommend recording your music tracks at a sample rate of 48kHz.
Q3. What is the sample rate of mp3?
Mp3 files have a sample rate of 44.1kHz.
Q4. At what sample rate does Spotify play music?
Spotify streams music at 44.1kHz and 16-bit.






























.png)