Most of us recognize USB-C cables as the handy connectors we use daily to juice up our devices. But there’s more to these cables. Beyond fueling up gadgets, they also have the potential to carry data, be it catchy tunes or high-definition videos. But can every USB-C cable out there do the magic of streaming video?
Well, not exactly. The ability to handle video doesn’t come standard with every USB-C cable. Only specific ones, equipped with something called an ‘alternate mode’ like the Display protocol, possess the knack to transmit video signals.
If you’re scratching your head thinking, “Alternate mode? Display protocol? How do I figure all this out with my cable?”, don’t fret. Dive into this article, and we will explore the mysteries of USB-C, exploring its various protocols, and generations.
Basics of USB-C: Protocols and Gens.
The USB-C cable is the advanced child in the USB family, designed to address both user convenience and technological advancements. Unlike its predecessors, USB-A, USB-B, Mini, and Micro, USB-C brings several distinguishing features to the table.

First, its C-shaped design makes it reversible and eliminates the guesswork when plugging it in. One doesn’t have to fiddle with orientations when plugging it in. Second, it serves a dual purpose, as it transfers both data and power. And the speed, with which it does, is unmatched in comparison to other USB types. For instance, its Thunderbolt 4 version supports data transfer rate of 40 Gbps and power delivery of 100 W.
Protocols
Communication via any two ports or devices is done through protocols. Since USB Cs were initially launched for power delivery, especially to charge our smart gadgets, the common protocol they all carry is Power Delivery (PD). It enables dynamic power adjustments and higher power levels up to 100W.
USB C may have optional protocols known as Alternate Modes (Alt Mode). They’re the one that makes a USB-C support video output and other capabilities beyond just USB.
Types/ Generations
USB C cables we see and use today weren’t the same in the past. They evolved over the years, and their capabilities and use cases have expanded.
USB 2.0 USB
These cables use USB-C connectors on both ends but only support USB 2.0 data speeds up to 480Mbps. They do not support any kind of video output and are only suitable for charging and syncing at regular USB 2.0 speeds.
USB 3.2 Gen 1 (Super Speed USB)
Also, sometimes listed as USB 3.0 or 3.1 cables. They can transmit data at up to 5Gbps which is the speed of USB 3.1 Gen 1. Like USB 2.0 cables, they do not support video-out signals.
USB 3.2 Gen 2
The fastest USB-only cables with data bandwidth of up to 20Gbps. This allows for quick file transfers and syncing. No video capabilities, however.
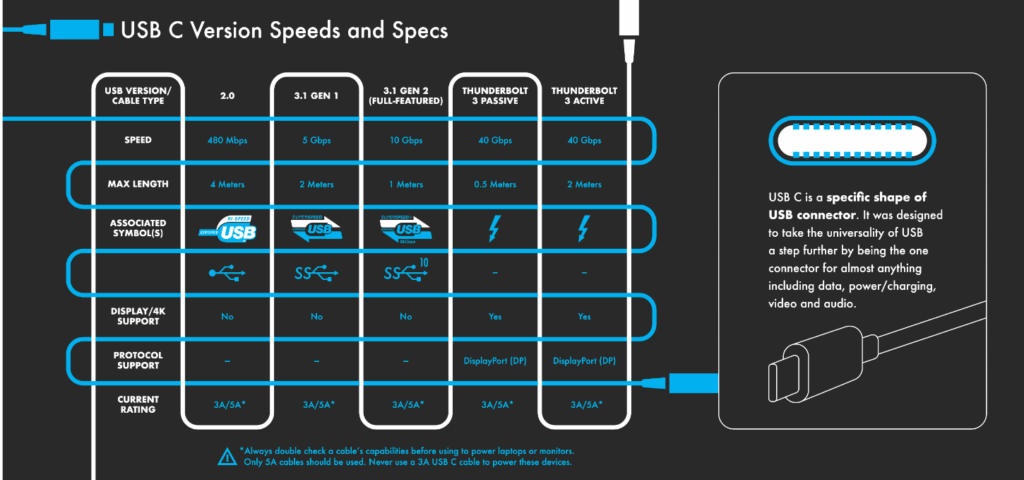
USB 4.0 /Thunderbolt USB-C Cables
Although using USB-C connectors, Thunderbolt cables are different. They carry PCIe video signals capable of dual 4K or single 5K displays. Thunderbolt integrates power, data, and video while supporting speeds up to 40Gbps and power delivery up to 100W. Thunderbolt cables are typically more expensive than standard USB-C versions.

USB-C and Video Support: The Burning Question
Now, let’s come to the burning question, Which type of USB C supports video? From the previous discussion, you may have got an idea of what’s the requirement for video support, right?
As said before, Alternate Mode (or Alt Mode) is a USB-C protocol that allows the cable to carry non-USB signals. It is through this protocol that USB-C achieves its video output capability. When a USB-C port and cable are configured with Alt Mode, they can transmit signals from standards such as DisplayPort, HDMI, or even Thunderbolt.
Different Alt Modes Available:
USB-C cables can use more than one way to send video signals. These different methods are called “Alt Modes”. Here are some of the main ones:
1. DisplayPort over USB-C:
This method is quite popular. It lets USB-C cables carry high-quality video and sound. When you hear about crisp and clear videos playing through a USB-C connection, it often means they use this mode.
2. HDMI Alt Mode:
Many of us know HDMI – it’s what we often use to connect our TVs to other devices. Some USB-C cables can use the HDMI protocol too. This means they can show videos on TVs or monitors that have HDMI ports. Some of these videos can be in super high quality, like 4K.
3. MHL Alt Mode:
Not everyone might have heard of this one. It’s special for some mobile devices. With this mode, phones or tablets can send very high-quality videos, again like 4K, directly to TVs.
4. Thunderbolt Mode (for devices that support Thunderbolt 3 & 4):
Think of Thunderbolt as a super-fast way to send data. Some fancy laptops and top-notch equipment have this. When a USB-C cable uses Thunderbolt mode, it can even send videos of the best quality available, like 8K, which is super sharp and detailed.
So, we conclude that although USB C Cables can support video support, not every cable has the ability. They need to have any of these Alternate modes for video support. Similarly, the port they’re connected should support that mode.
Identifying USB-C Cables That Support Video
Now, that you know all about the C cables that support video, the next thing is to physically figure out which cable does what. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure you select the right cable for your needs.
1. Manufacturer Specifications
The most direct way to confirm video support is by referring to the manufacturer’s specifications. Brands typically list out the capabilities of their cables. Look for terms like “Supports DisplayPort Alt Mode” or “HDMI Alt Mode Compatible”.
2. Cable Markings:
Quality USB-C cables often have symbols or markings on the connectors or cable itself. For instance, a tiny DisplayPort logo indicates that the cable supports DisplayPort over USB-C. Similarly, a thunderbolt cable has a thunderbolt sign on it.
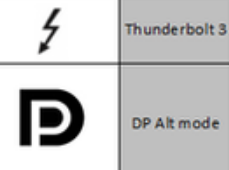
3. Product Reviews and User Feedback:
Before purchasing, it is a good practice to check product reviews and feedback from other users. These provide real-world insights into the cable’s performance and capabilities, helping you make an informed decision.
FAQs
Can all USB-C ports on devices handle video output?
No, not all USB-C ports support video output. The device’s port must support Alternate Mode (Alt Mode) to handle video.
Is there a difference between USB-C cables for smartphones and laptops concerning video support?
The form factor (smartphone or laptop) isn’t the determinant. What matters is the cable’s and the port’s specifications. Some smartphone USB-C cables might be designed mainly for charging and limited data transfer, while others can handle video output.
Will a USB-C cable supporting video also support faster data transfer and charging?
It’s not a criterion. However, all USB C cables that currently support video have high data transfer and charging rates. Consider, for instance, the USB 4.0, which supports video and can transmit power up to 100 W and data at the rate of 40 Gbps.
What is the maximum video resolution supported by USB-C?
The maximum resolution depends on the Alt Mode it supports and the device’s capabilities. For instance, DisplayPort over USB-C can support up to 8K resolutions, while HDMI Alt Mode might be limited to 4K depending on the version.
Conclusion
Not all USB C cables are cut from the same cloth. Some cables are just for charging, while others can transmit those stunning high-def videos. It’s all possible when they support Alt modes. They’re like the different languages a USB-C can speak, from DisplayPort to HDMI, and even the super-fast Thunderbolt. And, it is not just about the cable. The devices you are connecting play a massive part too.
If you’re ever in doubt about what a particular USB-C cable can do, just take a closer look at its sign. Does it have a display (D) or a thunderbolt? If it does, then that’s your video-supporting cable.
Since not every USB-C cable supports reliable video output, it’s essential to have a trusted monitor to clearly test and ensure proper visual signals. A portable camera monitor helps quickly verify cable compatibility and delivers seamless, high-quality video monitoring.






























.png)