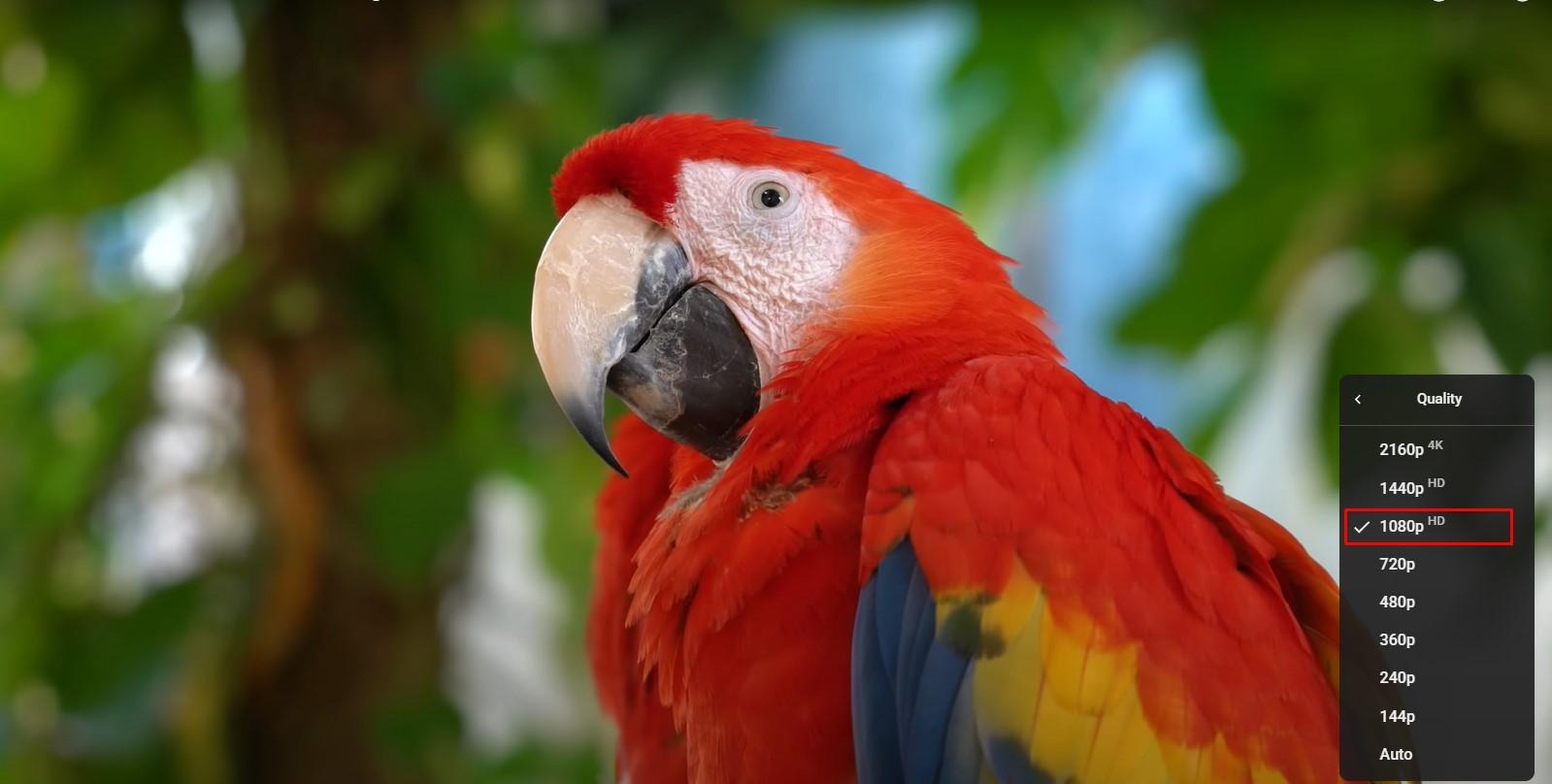
Ever wonder how your favorite show appears instantly when you hit play? Today’s digital landscape makes streaming feel effortless. Yet complex technology powers every frame you see.
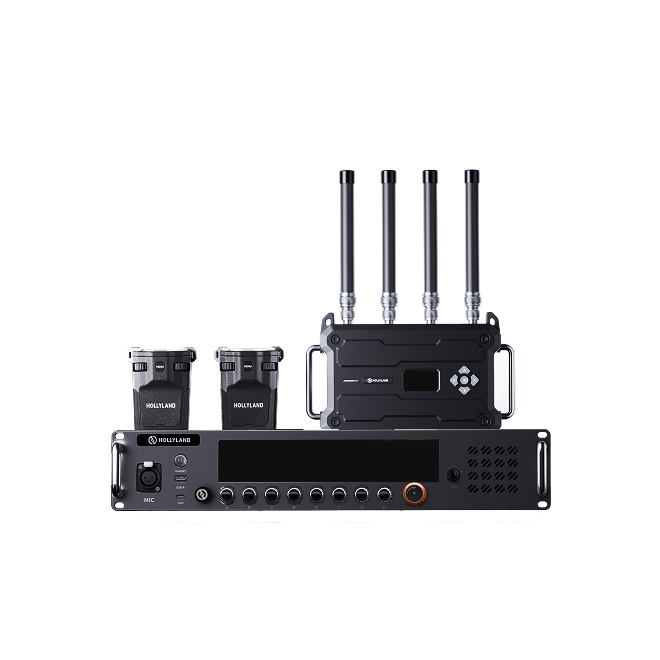
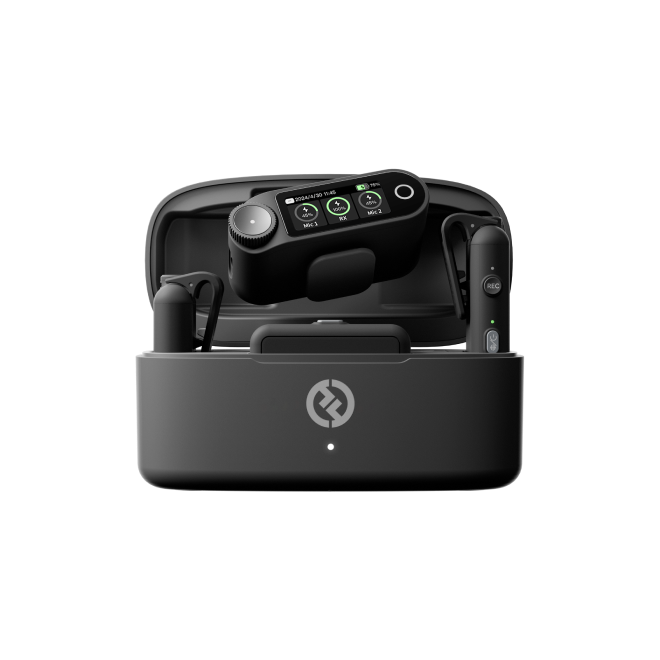
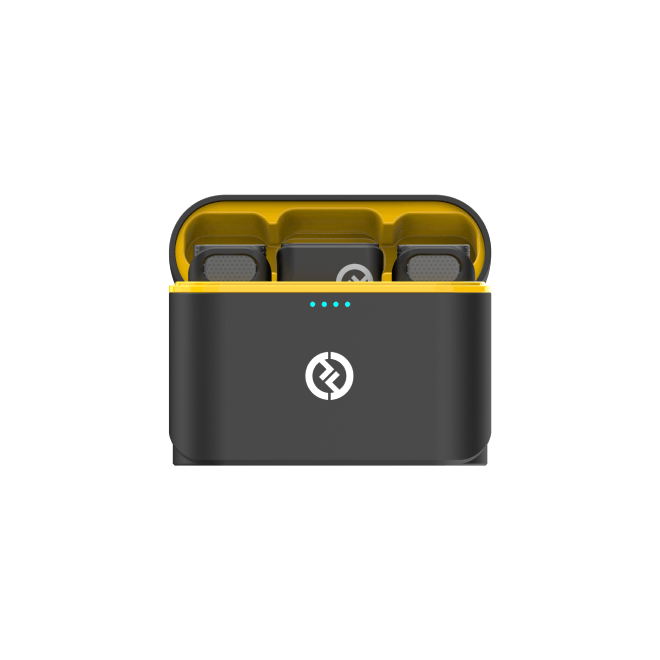
Today’s creators demand professional-grade streaming solutions. A streaming camera like the Hollyland VenusLiv Air delivers 4K quality at 30fps with reliable 24/7 streaming performance. With just a tap, you can stream Twitch, Facebook, or go live, without any computer connection.
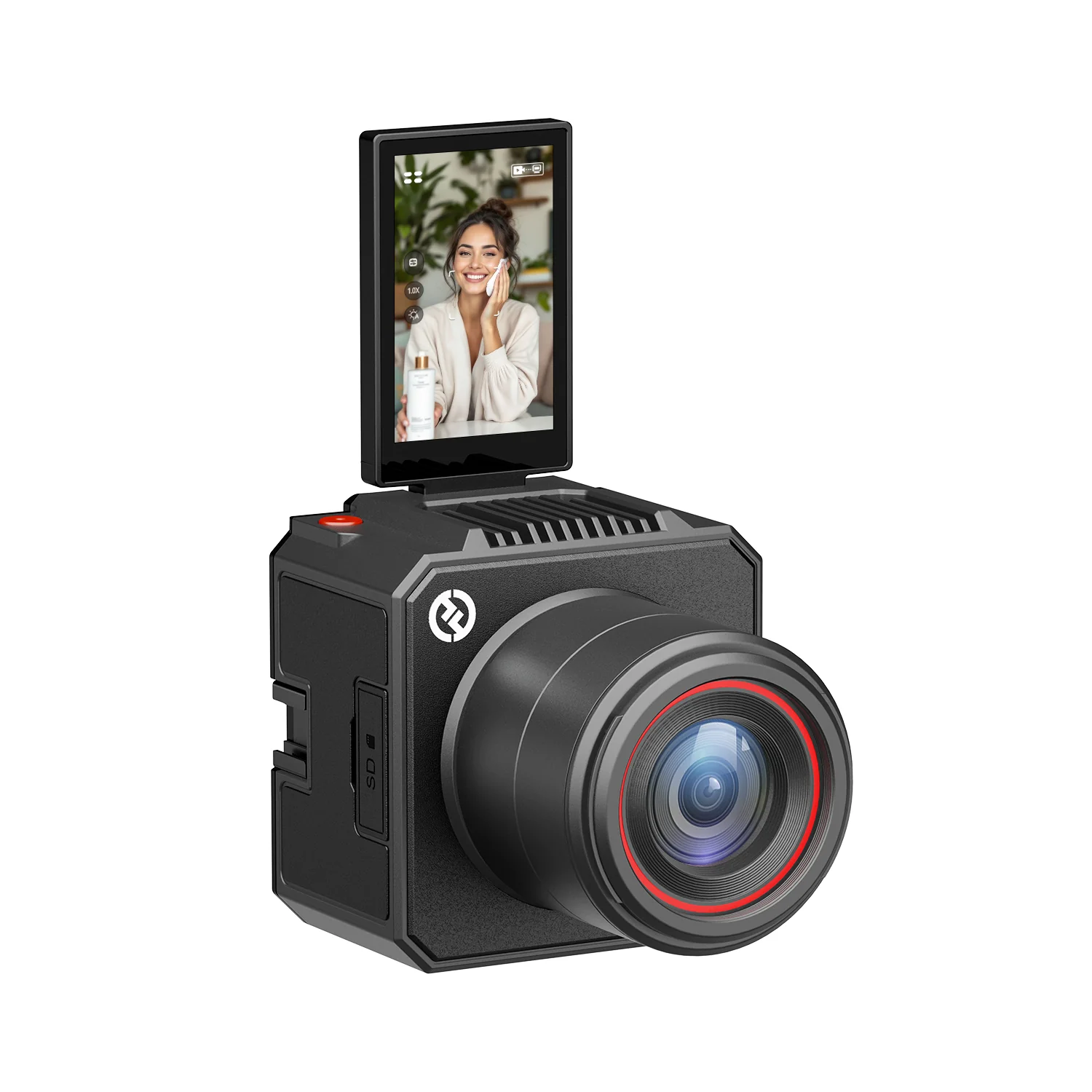


Hollyland VenusLiv Air - Compact 4K Streaming Camera
A compact, all-in-one 4K live streaming camera with a large sensor and fast lens, featuring AI-powered tools.
Key Features: 4K30 | 1/1.3″ CMOS | AI Tuning | 24/7 Streaming
Understanding how streaming works can transform your digital experience. So, in this article, we’ll break down how different types of streaming technologies work. Let’s get started and discuss further.
What is Streaming?
Streaming is a continuous process of real-time delivery of digital content in which a file (audio or video) is transmitted over the internet to the user’s device in chunks. The file being watched or played on the user’s device is stored remotely and transmitted over a few seconds in small data packets. That way, the file can be played without requiring it to be downloaded on the device.
In streaming, you don’t have to wait to view the file like in the traditional downloading process, but it needs a secure internet connection. Furthermore, as the content is not permanently stored on your device, it results in saving storage space.
Different Types of Streamings and How They Work
On-Demand Video Streaming
On-demand streaming delivers pre-recorded content whenever users want it. Perfect examples of popular platforms include Netflix and YouTube.
The technology works through content libraries stored on servers. When you click play, servers immediately begin transmitting video data packets.
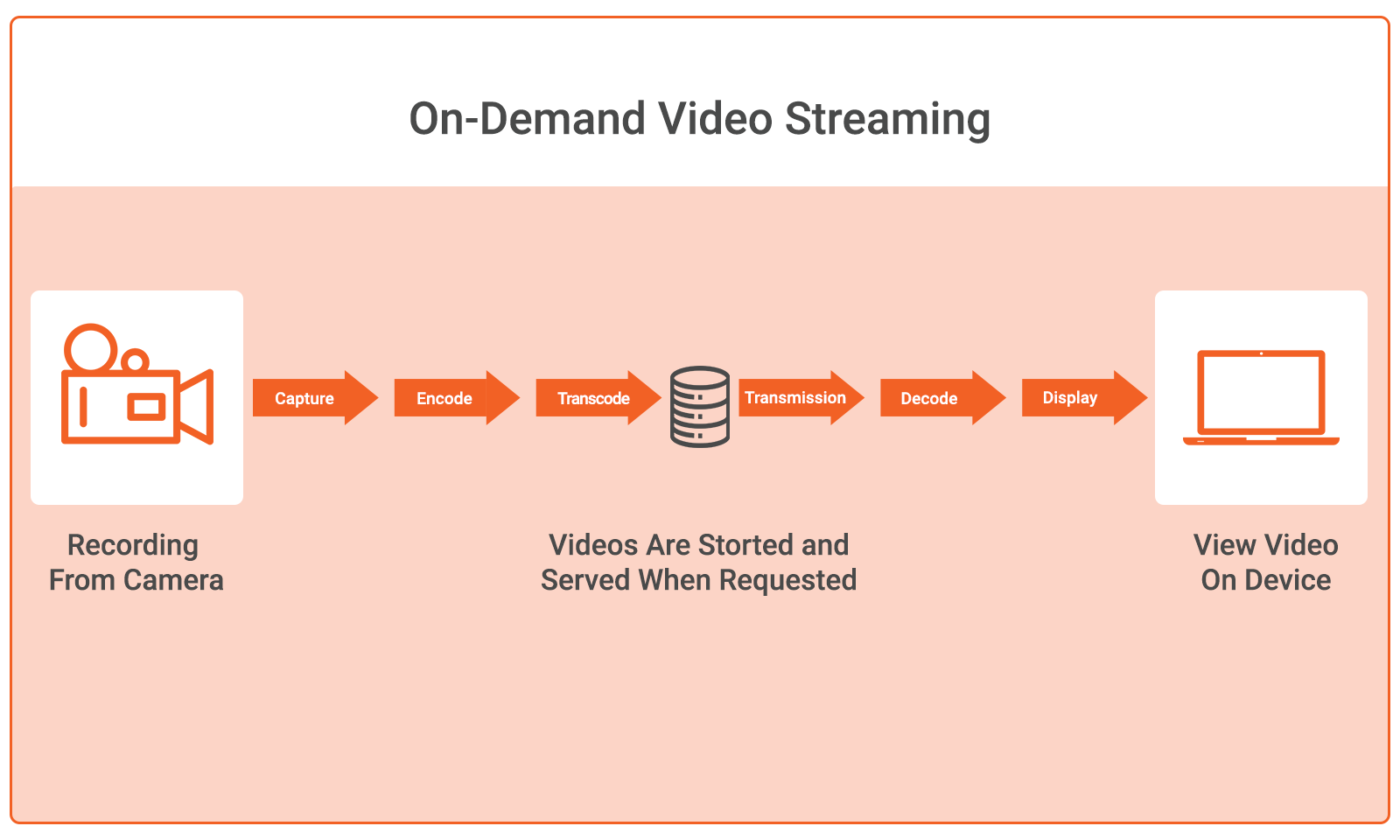
On-demand streaming offers three main business models:
- Subscription-based (SVoD): Monthly fees provide unlimited access
- Transactional (TVoD): Pay per movie or episode rental
- Ad-supported (AVoD): Free content with commercial interruptions
Live Video Streaming

Live streaming broadcasts events in real-time as they happen. In this method, viewers experience immediate transmission from source to screen.
The process involves capturing live footage, which is compressed by the encoders. The streaming servers then distribute content to thousands of viewers simultaneously.
Real-Time Streaming

This type of streaming minimizes delay by offering real-time communication. Its low latency remains under a few seconds, which optimizes performance. The technology establishes direct peer-to-peer connections. Information is thus not as slow as the old server-based technologies. Video conferencing applications such as Google Meet and Zoom incorporate real-time streaming.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming

Adaptive streaming is a dynamic technology that automatically adjusts the video quality according to your internet speed. On a slow connection, the system minimizes resolution in order to avoid buffering. On the other hand, higher-quality streams are allocated to faster connections.
The technology produces several copies of a video file. Various connection speeds are well supported with different bitrates.
Progressive Streaming

Progressive streaming allows content playback while downloading continues. Users can start watching immediately without waiting for complete file downloads.
The method works by downloading video segments sequentially. Meanwhile, media players begin playback with buffered portions. This approach bridges traditional downloading and modern streaming technologies. However, progressive streaming requires more storage space than pure streaming.
Audio Streaming

It delivers audio content in real-time. It includes music, podcasts, and radio content. Spotify serves as a good example of an audio streaming platform. It revolutionized music consumption through instant access to millions of tracks.
The stream works when the audio files are compressed using specialized codecs. AAC and MP3 formats balance quality with bandwidth efficiency effectively. With the smaller file sizes, transmission is faster over various internet connection speeds.
Best Platforms for Different Types of Streaming
With several streaming platforms, each one serves different needs. Here are some of the well-known platforms for different types of streaming.
Video-on-Demand (VOD) Streaming

- Netflix: It is a globally renowned subscription-based VOD with an extensive library of movies, TV shows, and documentaries.
- Disney+: Another subscription-based VOD dominates family entertainment, offering comprehensive parental controls and age-appropriate programming.
- Amazon Prime Video: It is especially for existing Prime members, featuring Dolby Atmos tracks and an expanding content library.
Live Streaming Platforms

- Twitch: It is a gaming live streaming platform with over 140 million monthly active users and strong community features.
- YouTube Live: It is popular for general live streaming across various niches.
- Facebook Live: Features social media integration for broadcast streaming.
Best Professional Live Streaming Tools

- StreamYard: Simple interface with direct social media streaming and real-time audience interaction
- OBS Studio: Extensive customization for professional-level streaming with third-party plugin support
- Wirecast: Comprehensive production capabilities, including instant replays and audience polls
Best Multi-Platform Streaming

- OneStream: Offers simultaneous streaming across 45+ social media platforms, plus simultaneous web streaming.
- Be.Live: Features professional multi-platform streaming.
Music Streaming Platforms

- Tidal: Delivers superior hi-res audio quality with 24-bit/192kHz FLAC streams and Dolby Atmos support.
- Apple Music (for iOS Users): Seamlessly integrates with Apple devices and offers lossless streaming with Spatial Audio features.
- Spotify (Free Tier): Best free option with ads and music discovery features
Specialized Streaming Platforms

- Brightcove: Professional video hosting and streaming platform with enterprise security and analytics.
- Wistia: Specializes in marketing teams with lead-generation tools and professional branding features.
Conclusion
To conclude, streaming has transformed how we consume content. Complex data packets travel instantly across networks, and you can watch content without downloading it. Different streaming types serve specific use cases and technical requirements. Understanding how the working will help content creators and consumers make informed platform choices.
FAQs
How does streaming differ from downloading?
Streaming plays content immediately while data arrives in small chunks from servers. Downloading saves complete files to your device, allowing you to watch or listen to them.
What factors slow down streaming?
The most frequent streaming problems are slow internet speed, network congestion, and weak Wi-Fi signals. Playback problems may also be caused by high server traffic and outdated devices.
What is buffering?
Buffering is a feature that temporarily stores several seconds of content before what you are viewing. This avoids disruptions in the video when your internet connection is momentarily delayed or stuttering.






























.png)