In the symphony of sound recording, there exists a silent wizard – the phantom power microphone. This enigmatic device is the secret behind the crystal-clear vocals, the soul-stirring melodies, and the immersive audio experiences that grace our ears. Step into the realm of audio wizardry as we unveil the mystique of phantom power microphones, from their electrifying origins to their spellbinding applications. Prepare to be spellbound by the magic of sound!

But what exactly is a phantom power microphone, and how does it work? In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of phantom power microphones, explaining their concept, functions, applications, and much more.
What is a Phantom Power Microphone
A phantom power microphone, often referred to as a condenser microphone, is a type of microphone that requires an external power source to operate. Unlike dynamic microphones, which are passive and do not need additional power, condenser microphones are highly sensitive and rely on this external power, typically provided by mixing consoles, audio interfaces, or dedicated power supplies.

How Does Phantom Power Work?
The concept of phantom power may initially come across as enigmatic, but its functionality is, in fact, quite straightforward and rooted in the fundamentals of electrical engineering. This ingenious system serves as the lifeblood of condenser microphones, providing the necessary electrical energy to capture audio with exquisite detail and precision. Let’s embark on a comprehensive journey into the workings of phantom power and explore its key components in detail.
At its core, phantom power is a mechanism devised to supply a low-voltage Direct Current (DC) electrical signal to a microphone. This electrifying infusion of energy is achieved through the very same balanced audio cable used to transmit the audio signal. The DC voltage itself typically hovers around 48 volts, although variations do exist, generally falling within the range of 12 to 48 volts. These voltage fluctuations are dependent on the microphone’s specifications and the specific equipment in use.
The key components of phantom power include:
- Power Source: The beating heart of phantom power lies in its power source. This can take various forms, including a mixing console, an audio interface, or a dedicated phantom power supply unit. These sources act as the generators of the electrical current that will ultimately empower the microphone.

- XLR Cable: The secret conduit through which phantom power travels is the balanced XLR cable. This remarkable cable performs a dual role, acting as both the messenger of the audio signal and the carrier of the electrifying phantom power. Its balanced configuration is vital in ensuring the integrity of the audio signal while safely transmitting the DC voltage.

- Microphone: The pièce de résistance of this orchestration is the condenser microphone itself. Unlike its dynamic microphone counterpart, the condenser microphone relies on phantom power for its operation. Within its delicate frame lies a diaphragm, an essential component that transforms sound waves into electrical signals. When phantom power is activated, this voltage polarizes the diaphragm, priming it to respond to incoming audio waves. Additionally, the microphone’s internal amplifier amplifies these signals, rendering them ready for further processing.
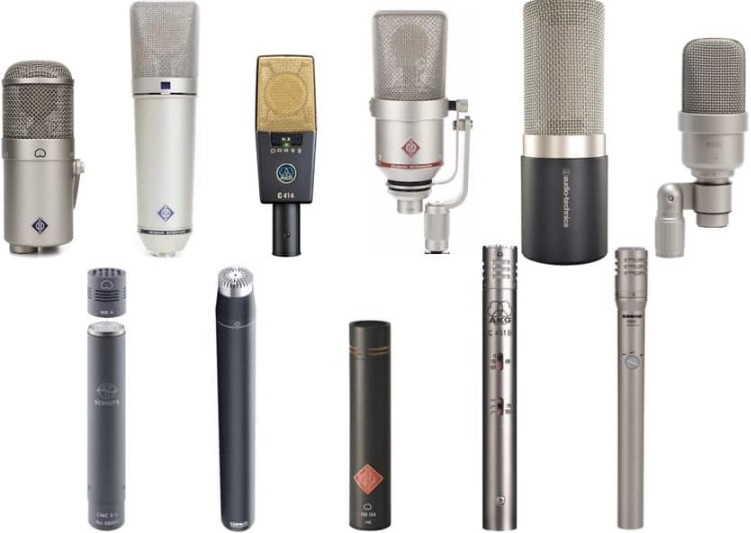

When the phantom power is engaged, the microphone’s internal circuitry uses this low-voltage DC power to polarize the microphone’s diaphragm and amplify the incoming sound waves. This polarization and amplification result in the microphone’s exceptional sensitivity and clarity, making it an ideal choice for recording vocals, acoustic instruments, and other nuanced sound source
Phantom Power Setup
Phantom power, often denoted as +48V or P48, serves as an ingenious solution for energizing microphones, eliminating the need for cumbersome external power supplies, as seen with tube microphones. Instead, it elegantly channels the essential DC electrical current through a balanced XLR cable. This voltage is indispensable, breathing life into the microphone’s diaphragm and internal amplifier. Activating phantom power sends a stream of DC current coursing through the XLR cable, providing the necessary voltage for the microphone’s operation.
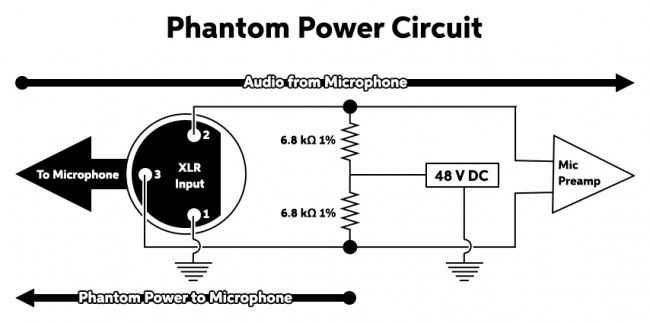
This power method finds its widest application in fueling condenser microphones, renowned for their active electronics. Notably, true condenser microphones (in contrast to electret) demand voltage for polarizing the microphone’s transducer element. In this realm, phantom power emerges as the dual-purpose solution, providing the voltage required for both these vital functions. It’s the unsung hero that empowers the world of pristine audio capture.
Applications of Phantom Power Microphones
Phantom power microphones find applications in various professional audio recording scenarios due to their exceptional performance. Here are some common uses:
Studio Recording
Within the hallowed confines of recording studios, phantom power microphones have established themselves as indispensable tools, akin to the artist’s brush and canvas. These marvels of audio capture prowess are entrusted with the noble task of immortalizing the subtlest vocal inflections, the resonance of acoustic guitars, the reverberations of pianos, and the intricate melodies of various acoustic instruments.

With their wide-reaching frequency response, these microphones embark on a relentless quest for sonic precision. Every note, every whisper, and every emotional resonance is etched into the annals of music production history with unparalleled detail and accuracy, making phantom power microphones an unrivaled ally for music creators.
Live Sound
In the realm of live sound reinforcement, phantom power microphones shine as the go-to choice. Their widespread adoption stems from their ability to capture the intricate nuances inherent in live performances. They become the sonic eyes and ears, faithfully reproducing the singer’s emotive vocals and the delicate subtleties of acoustic instruments. Condenser microphones, with their sensitivity and precision, rise as the preferred companions on stage, ensuring that every note and vocal flourish is conveyed to the audience with finesse and clarity.

Broadcast and Podcasting
Within the dynamic sphere of broadcasting and podcasting, condenser microphones reign supreme, cherished for their unparalleled capability to render voices with crystal-clear clarity and precision. These microphones stand as essential tools in the arsenal of content creators, enabling the crafting of professional-grade audio content. With their acute sensitivity and faithful sound reproduction, they transform every spoken word, every nuance, and every whisper into a tapestry of sound that captivates listeners and elevates the art of storytelling to new heights.

Field Recording
Sound designers and field recordists wield phantom power microphones as their sonic brushes, painting immersive landscapes of environmental sounds, wildlife calls, and the symphony of natural ambience. These microphones, celebrated for their remarkable sensitivity and knack for capturing the most delicate nuances, are indispensable tools in these creative endeavors. They become the ears of the wilderness, preserving the intricate details and subtleties of nature’s voice for our auditory exploration and artistic expression.

Types of Phantom Power Microphones
Phantom power microphones come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored to specific recording needs:
1. Large-Diaphragm Condenser Microphones
Large-diaphragm condenser microphones are known for their warm and rich sound, making them ideal for recording vocals and solo instruments. They excel in capturing low-frequency details.

2. Small-Diaphragm Condenser Microphones
Small-diaphragm condenser microphones offer greater accuracy in reproducing high-frequency sounds and are often used for recording acoustic instruments like violins, acoustic guitars, and percussion.

3. Shotgun Microphones
Shotgun microphones have a highly directional pickup pattern, making them perfect for capturing sound from a specific direction while rejecting background noise. They are commonly used in film and video production.

4. Lavalier Microphones
Lavalier microphones, also known as lapel microphones, are small condenser microphones often clipped to clothing. They are popular in broadcast journalism, interviews, and live presentations.

Choosing the Right Phantom Power Microphone
Selecting the right phantom power microphone depends on your specific recording needs. Consider factors such as the sound source, environment, and budget. It’s essential to research and test different microphones to find the one that best suits your requirements.
Studio Sanctuaries
In controlled studio environments, you have the luxury of using sensitive large-diaphragm condenser microphones that thrive on quiet, controlled acoustics.
Live Concert Halls
Live sound situations demand rugged microphones with excellent feedback rejection. Shotgun microphones and dynamic microphones are often preferred for their durability and noise-reduction properties.
Podcast and Broadcasting Studios
Sound-treated spaces benefit from condenser microphones that can capture your voice with pristine clarity. Pop filters and shock mounts can further enhance recording quality.
On-the-Go Adventures
Field recording requires portable, robust microphones designed to withstand the elements. Shotgun and small-diaphragm condenser microphones are versatile choices for outdoor recordings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phantom Power Microphones
Like any technology, phantom power microphones come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Exceptional Sound Quality: Phantom power microphones offer high sensitivity and wide frequency response, resulting in clear and detailed audio recordings.
- Versatility: They are suitable for various recording applications, from studio work to live sound reinforcement.
- Durability: Condenser microphones are generally built to last, making them a reliable investment for professionals.
Disadvantages
- Power Requirement: They rely on external power sources, which means you need compatible equipment for them to function.
- Price Range: High-quality phantom power microphones can be expensive, but there are budget-friendly options available.
Common Myths About Phantom Power Microphones
There are several misconceptions surrounding phantom power microphones. Let’s debunk a few of them:
Myth 1: Phantom Power Can Damage Dynamic Microphones
This myth, circulating in the audio world, claims that phantom power poses a peril to dynamic microphones. However, let’s set the record straight: this notion is entirely false. Dynamic microphones are robust and resilient, designed to withstand the rigors of live sound and studio environments.
They are impervious to the charms of phantom power, and you can confidently pair them with equipment that provides this voltage without a trace of concern. In fact, dynamic microphones and phantom power often coexist harmoniously, offering reliable performance and pristine audio capture.
Myth 2: All Condenser Microphones Need 48V Phantom Power
Dispelling another common misconception, it’s essential to recognize that not all condenser microphones are bound by the universal rule of requiring 48V phantom power. While this voltage level is indeed prevalent, the audio world is a diverse landscape, and some condenser microphones are content with lower voltages.
Therefore, a prudent approach is to always consult the microphone’s specifications to ensure it receives the precise amount of phantom power it demands. This keen attention to detail guarantees optimal microphone performance and audio quality.
Conclusion
In the intricate world of audio recording, understanding the role of phantom power is essential. It’s the life force that powers condenser microphones, elevating your audio recordings to new heights of clarity and precision. From studio vocals to the subtlest of field sounds, phantom power is the unsung hero of audio capture.
As you embark on your audio journey, remember that dynamic microphones are sturdy workhorses, while ribbon microphones require cautious handling with phantom power. For condenser microphones, phantom power is their lifeblood. Matching your microphone’s needs with your equipment is the key to harmonious audio capture.
Did this article clarify your doubts about phantom power microphones? Share your thoughts, questions, and feedback with us. Your insights help us refine our content and serve you better. Leave your comments and reviews below.
When choosing audio equipment, it’s important to pick the right mic setup depending on your scenario. If you prefer freedom of movement without compromising audio quality, a wireless lavalier microphone can be perfect – offering convenience and crystal clear wireless audio without needing phantom power.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need phantom power for a dynamic microphone?
No, dynamic microphones do not require phantom power. However, some low-output dynamic mics, like the Shure SM7B, may need a preamp to boost the signal, and if that preamp is active, you’ll need to turn on phantom power.
Can you damage a ribbon microphone with phantom power?
Active ribbon mics need phantom power, but passive ribbon mics should never be connected to a preamp with phantom power. Miswiring XLR cables or hot-patching on a TRS patch bay can damage passive ribbon mics.
Do condenser mics need phantom power?
Yes, condenser microphones are more sensitive and typically require phantom power to operate. Some exceptions exist, but they’re less common.
How is phantom power supplied?
Phantom power is delivered via a 48-volt Direct Current (DC) voltage transmitted through the microphone cable. This essential voltage source typically originates from a mixer or audio interface and can be conveniently activated or deactivated, safeguarding your microphone from potential damage.
Why is it called phantom power?
The term “phantom power” is derived from its intriguing ability to carry both power and audio signals through the same cable simultaneously. This dual function creates the illusion that the power source remains hidden or “phantom,” seamlessly merging with the audio signal within the confines of a single cable, simplifying audio equipment setups and connections.
Can I use a condenser mic without phantom power?
No, condenser microphones are like high-performance cars, they need fuel, and in their case, that fuel is phantom power. Without it, they can’t generate the audio signals that make them exceptional. Phantom power is the lifeblood that polarizes the microphone’s diaphragm, allowing it to capture sound with precision and clarity. So, in short, no phantom power means no audio from a condenser microphone.
What are the benefits of phantom power?
Phantom power is primarily used for condenser microphones with active electronics. It also polarizes the transducer element in true condenser mics (not electret), ensuring accurate sound capture.
Can phantom power damage a microphone?
Phantom power won’t harm most microphones that don’t require it, as they typically reject it. Ribbon microphones are an exception, so it’s essential to handle them with care.
Do XLR mics need phantom power?
Mics with XLR connectors generally expect phantom power, but some may require bias power or none at all. Matching your microphone’s requirements with your equipment is crucial.
How long can phantom power run?
Assuming no cable shorts, phantom power can run through hundreds of feet of cable, potentially even thousands of feet with quality cable and connectors.
What is the maximum voltage for phantom power?
Phantom power typically ranges from 12 to 48 volts, with microphones drawing the current they need based on their specifications.
Which type of microphone should never receive phantom power?
Vintage ribbon microphones and mics wired for unbalanced (high-impedance) operation can be damaged by phantom power unless modified accordingly.
What is the difference between a preamp and phantom power?
A preamp amplifies the microphone signal, while phantom power supplies the necessary power for the microphone to function. They serve distinct roles and are separate components in the audio chain. For condenser microphones to work, they must receive 48V phantom power.






























.png)