Many confuse gain with volume because both make the mic louder and result in distorted recordings. Generally, microphone gain amplifies and determines the mic’s signal sensitivity when it reaches the speaker or recording software. Therefore, knowing how to set mic gain is crucial for content creators to improve the sound quality.
This article will clarify microphone gain and how it ensures crisp and crystal-clear audio for your recordings.
What is Microphone Gain?
Sometimes, microphones have low-voltage audio output and must be amplified to boost their production and make it audible. So, the purpose of gain is to amplify the audio signal captured by the microphone to ensure vocal clarity. It’s measured in decibels (dB) and can be adjusted by using the gain knob or slider on your mixer or audio interface.
Microphone gain ensures the audio signal is strong enough to be processed without distortion while avoiding noise from excessive amplification. If the gain is too low, the recorded audio will require additional amplification, which introduces noise. On the other hand, if the gain is too high, the audio may become clipped or distorted, resulting in background or unpleasant noises.
How Microphone Gain Works
The signal flow is the path the audio signal takes from the microphone until it reaches the amplifier to boost its strength. Therefore, modifying the gain levels and attaining the best sound quality requires comprehending this flow. Here’s the simple process of how microphone gain works:
Microphone: First, the microphone captures and converts the acoustic energy into electrical energy.
Preamplifier: This captured weak signal is sent to the preamplifier, which amplifies the microphone-level signal to line level. The preamplifier boosts the microphone signals for further processing without disturbing their quality.
Audio Interface or Mixer: The interface processes the signal before sending it to the equalizer, compressor, and mixer for adjustment, processing, and routing to the amplification system. Sometimes, before the interface, the signal may pass through the channel strip or processor before the output to retain signal quality.
How Preamps Adjust Gain Levels
Preamps are crucial for adjusting gain levels. They amplify the low-level audio signals from the mic before sending them to the amplifier, ensuring a strong and balanced mic gain without introducing significant noise or distortion. Moreover, the mic preamp allows you to adjust the gain level depending on the sound source you are capturing.
How to Set up Microphone Gain?
Setting your microphone gain is crucial to ensure you’re heard loud and clear without distortions.
Monitoring
First, before plugging in your microphone, ensure you mute the monitors. If you plug in a microphone with a monitor or phantom power switched on, a loud popping or screeching sound will be produced, affecting your ears or speakers. Therefore, keep the monitors muted until phantom power is set or your mic is plugged in, then unmute them and start listening.
Press the PFL Button on your Mixer

Due to space constraints, many small mixers or consoles do not have level meters in each channel. Therefore, using the PFL (Pre-Fader Listening) or SOLO button can isolate the mic signal you are adjusting the gain of without affecting the central mix. It allows you to use the main level meter to adjust the gain without impacting the fader settings.
Channel Strips and External Preamps
If using external preamps or channel strips, its output should be connected to the audio interface or mixer input. Deactivate the EQ, compressor, and other settings when using the external preamp because they can affect the level. However, if your built-in interface lacks power or you use low-output microphones, external preamps will allow you to achieve optimal sound quality.
Finding the Right Gain Settings
While level meters are crucial for setting mic gain, listen closely to the audio signal as you gradually increase the gain. If the gain is too low, the microphone’s noise floor will be noticeable, resulting in unclear sound. Therefore, listen out to achieve the correct gain for maximum vocal clarity and track potential problems.
Gain vs. Volume: Key Differences

Volume is defined as the audio device’s output (decibels dB). Increasing the volume increases the loudness of the sound. It changes the strength of the processed audio signal, and changing the volume does not affect its tone but changes its loudness.
For instance, if you project sound at a consistent level, the loudness of the audio can vary as you adjust the volume. Volume is the strength of sound waves and is a personal preference setting. Unlike microphone gain, increasing the volume will not distort the recording unless it is distorted from the source.
Conversely, the gain is the input dB, significantly altering the audio signal’s strength before processing. It adjusts the microphone sensitivity, and changing the gain changes the audio signals to work with. Microphone gain impacts the tone, clarity, and noise because too much gain introduces audio distortions.
Common Problems with Microphone Gain and How to Fix Them
When setting microphone gain, several common mistakes can lead to audio issues and negatively impact the recording’s quality. Therefore, understanding these problems will help you avoid them and achieve better audio. Here are some common pitfalls and how to fix them effectively:
Clipping or Distorted Audio
If the gain is set too high, it exceeds the system limit, resulting in distorted or clipped audio. Some mics are sensitive, and singing or placing them close to the instruments may overload the audio input. It’s necessary to control the gain level on your audio interface and monitor the levels with a peak meter.
Setting the Gain To Low
Audio signals become weak if the gain is too low, and boosting the signal later introduces noise. To avoid clipping, increase the gain from your audio interface or preamp to a desirable level. For better audio, use an external preamp, check the audio settings on your interface or amplifier, or use a higher output mic.
Understanding the Source Dynamics
Different sound sources have different dynamic ranges, requiring different microphone gain settings. Ignoring the dynamics of your sound source may result in sudden spikes or dips in your audio recordings. Therefore, understand the loudness variations in your sound source and adjust the gain accordingly to achieve vocal clarity.
Excessive Background Noise
Neglecting room reflections or setting the gain high can introduce background noises, which affect the overall sound quality. To reduce unnecessary noises, use a directional microphone, lower the gain, and increase mic proximity. Furthermore, listen to the audio in real time with headphones and make precise gain adjustments.
Note: Choose wireless microphones like Hollyland Lark M2S to adjust the microphone gain through an intuitive app. Hollyland Lark M2S’s titanium build and logo-free design deliver balanced and detailed-rich audio and minimizes distortions and background noises. Furthermore, besides the app, use the knob on transmitters to adjust the volume gain with three levels. So, the premium gain controls and intelligent noise cancellation features allow you to avoid common gain problems.
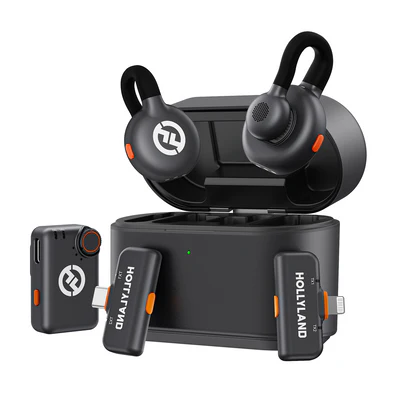


Hollyland LARK M2S - Wireless Hidden Microphone
An ultra-discreet wireless microphone featuring a clip-on transmitter for an “invisible” fit.
Key Features: No-Logo Fit | Ti+ Design | 48 kHz/24-bit
Conclusion
Microphone gain amplifies audio signals to achieve crystal-clear recordings. Understanding how microphone gain works can help you set up the microphone for optimal performance. Additionally, carefully adjusting microphone gain and avoiding common mistakes ensure professional-grade recordings and live audio. Experimenting with different gain settings and implementing proper adjustments can enable you to record quality audio.
Understanding microphone gain helps you unlock clear audio quality right from the start, especially if you’re recording speech or interviews remotely. A wireless lavalier microphone, for example, provides optimal gain levels and ensures your subject’s voice remains crisp and distortion-free even from a distance.
FAQs
Why is proper gain setting important?
Proper gain settings ensure balanced, clean, high-quality audio without distortion or background noise. By striking an optimal balance, you can minimize distortions or clipping, reduce background noise, and maintain a proper signal-to-noise ratio. So, adequate gain settings ensure consistent audio quality during recordings or live performances.
What happens if the microphone gain is too high?
If the microphone gain is too high, it causes distortion and clipping, affecting the overall audio quality. With high gain, the microphone amplifies the background noises and picks up sound from the speakers.
Can I use microphone gain to fix a low-volume recording?
Gain cannot fix low-volume recordings after they are recorded because gain works at the input level. Microphone gain controls how much audio signal is amplified before processing or recording. Therefore, increasing gain after the recording will not restore the lost audio details but will introduce distortions and noise.
Is it possible to use software or tools to adjust microphone gain?
Using multiple tools and software has made adjusting and controlling the microphone gain easier, but it depends on your hardware and compatibility. However, you can use an audio interface, external preamps, digital audio workstations, and software for clean audio. So, prioritize quality, compatibility, and ease of use for efficient microphone gain control.






























.png)